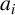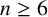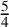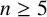Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419506 results in Open Access
THE JOURNALS OF GEORGE GREY, 1835–1838: BOOK THREE
-
- Journal:
- Royal Historical Society Camden Fifth Series / Volume 69 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2025, pp. 135-209
- Print publication:
- July 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Trauma Levels and Religious Coping of Earthquake Survivors with Chronic Diseases
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 19 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2025, e134
-
- Article
- Export citation
The landscape of the Zanj Rebellion? Dating the remains of a large-scale agricultural system in southern Iraq
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
IMPROVED LOWER BOUNDS FOR STRONG n-CONJECTURES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 119 / Issue 1 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2025, pp. 61-81
- Print publication:
- August 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
THE CORRESPONDENCE OF GEORGE GREY
-
- Journal:
- Royal Historical Society Camden Fifth Series / Volume 69 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2025, pp. 259-300
- Print publication:
- July 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Family Ties, Social Control, and Authoritarian Distribution to Elites
-
- Journal:
- American Political Science Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2025, pp. 1-19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
INTRODUCTION
-
- Journal:
- Royal Historical Society Camden Fifth Series / Volume 69 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2025, pp. 1-13
- Print publication:
- July 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of supplementation with vitamin D on biochemical markers of iron status and erythropoiesis in older people: BEST-D trial
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 134 / Issue 1 / 14 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2025, pp. 28-34
- Print publication:
- 14 July 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
James E Atwell, Reimagining at the Sources: Probing the Story of Israel from its Origins to Jesus of Nazareth (T&T Clark: 2024), xv + 381 pp. 978-0-567-71191-5. Hb, £130.00 (pb forthcoming)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Anglican Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2025, pp. 1-4
-
- Article
- Export citation
Amber Networks in Prehistory: North-Eastern Iberia as a Case Study
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Archaeology / Volume 28 / Issue 4 / November 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2025, pp. 405-422
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
To write or not to write: the literary strategies of British civil engineers in the late eighteenth century
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal for the History of Science , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2025, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Halberds of power: an Early Bronze Age hoard from Muszkowo in Poland
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
RHC volume 69 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Royal Historical Society Camden Fifth Series / Volume 69 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2025, p. b1
- Print publication:
- July 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Aquinas on Scripture: A Primer by John F. Boyle, Emmaeus Academic, Steubenville, OH, 2023, pp. 138, $26.95, hbk
-
- Journal:
- New Blackfriars / Volume 106 / Issue 5 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2025, pp. 458-460
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Identifying Health Care Access Gaps in Areas of Oregon at High Risk of Respiratory Hospitalization During Wildfires
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 19 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2025, e133
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
I SEE YOU: AN OVIDIAN ACROSTIC (REM. AM. 681–5) AND CATULLAN ACROSTICS
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Quarterly , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2025, pp. 1-5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
PREFACE
-
- Journal:
- Royal Historical Society Camden Fifth Series / Volume 69 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2025, pp. vii-viii
- Print publication:
- July 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
THE JOURNALS OF GEORGE GREY, 1835–1838: BOOK ONE
-
- Journal:
- Royal Historical Society Camden Fifth Series / Volume 69 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2025, pp. 73-104
- Print publication:
- July 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
EDITORIAL PRINCIPLES
-
- Journal:
- Royal Historical Society Camden Fifth Series / Volume 69 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2025, p. 15
- Print publication:
- July 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Tulaneia amabilia n. gen. n. sp.: a new erniettomorph from the Wood Canyon Formation, Nevada and the age of the Ediacaran–Cambrian transition in the Great Basin
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 98 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2025, pp. 929-951
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation