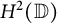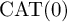Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1397622 results in Open Access
African Views of Chinese Engagement: The Political Economy of a Gender Gap
-
- Journal:
- Politics & Gender / Volume 21 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 246-274
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Matthew Gmalifo Mabefam. Witch Camps and Witchcraft Discourse in Africa: Critiquing Development Practice. Lanham, MD: Lexington Books, 2023. 191 pp. Preface. Acknowledgment. List of Abbreviations. Glossary. Bibliography. Index. $95. Hardcover. ISBN: 9781666918496.
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 68 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 382-383
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Joshua Grace. African Motors: Technology, Gender, and the History of Development. Durham, NC: Duke University Press, 2021. 432 pp. $31.95. Paper. ISBN: 978-1-4780-1171-2.
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
SAP volume 38 issue 2 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Studies in American Political Development / Volume 38 / Issue 2 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Aberrant controllability of functional connectome during working memory tasks in patients with schizophrenia and unaffected siblings
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 227 / Issue 1 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 463-472
- Print publication:
- July 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Infants of diabetic mothers: epidemiology, pathophysiology, fetal heartassessment, structural and functional heart consequences: A narrative review
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 10 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 2068-2073
-
- Article
- Export citation
David Smilde, Verónica Zubillaga, and Rebecca Hanson (eds), The Paradox of Violence in Venezuela. Revolution, Crime, and Policing During Chavismo. Pittsburgh, PA: University of Pittsburgh Press. 2022. Notes, bibliography, index, 312 pp.; hardcover $55.
-
- Journal:
- Latin American Politics and Society , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 1-4
-
- Article
- Export citation
Unveiling a new species of Trapania (Gastropoda: Nudibranchia: Goniodorididae) from the South-eastern Pacific using anatomical and molecular tools
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 104 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, e121
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Bounds for equilibrium states on amenable group subshifts
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 45 / Issue 8 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 2414-2438
- Print publication:
- August 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A new record of the nudibranch Halgerda batangas from Vietnam confirmed by DNA barcoding
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 104 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, e120
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nearly invariant Brangesian subspaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 68 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 318-337
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Restricted Euler dynamics in free-surface turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1002 / 10 January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, A38
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Isolated pulmonary valve endocarditis leading to right ventricular outflow obstruction
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 12 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 2709-2711
-
- Article
- Export citation
PROPER
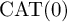 $\mathrm {CAT(0)}$ ACTIONS OF UNIPOTENT-FREE LINEAR GROUPS
$\mathrm {CAT(0)}$ ACTIONS OF UNIPOTENT-FREE LINEAR GROUPS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 2 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 587-601
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Militarism and Law in Africa: A Governing Paradox
-
- Journal:
- Law & Social Inquiry / Volume 50 / Issue 2 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 621-628
- Print publication:
- May 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
COVID-19 outbreaks in nursing homes in Los Angeles County, March 2020–April 2022
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 46 / Issue 2 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 136-142
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
A pilot tagging study of yellownose skate (Dipturus chilensis) and roughskin skate (Dipturus trachyderma) off southern Chile
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 104 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, e123
-
- Article
- Export citation
Labor Union Membership and Women’s Political Ambition: Evidence from the United States
-
- Journal:
- Politics & Gender / Volume 21 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 220-245
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A review of the effectiveness of short-time work programmes: The Spanish case from a comparative perspective
-
- Journal:
- The Economic and Labour Relations Review / Volume 35 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 1000-1030
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation