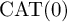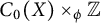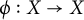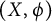Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418337 results in Open Access
PROPER
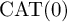 $\mathrm {CAT(0)}$ ACTIONS OF UNIPOTENT-FREE LINEAR GROUPS
$\mathrm {CAT(0)}$ ACTIONS OF UNIPOTENT-FREE LINEAR GROUPS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 2 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 587-601
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Militarism and Law in Africa: A Governing Paradox
-
- Journal:
- Law & Social Inquiry / Volume 50 / Issue 2 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 621-628
- Print publication:
- May 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
COVID-19 outbreaks in nursing homes in Los Angeles County, March 2020–April 2022
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 46 / Issue 2 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 136-142
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
A pilot tagging study of yellownose skate (Dipturus chilensis) and roughskin skate (Dipturus trachyderma) off southern Chile
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 104 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, e123
-
- Article
- Export citation
Labor Union Membership and Women’s Political Ambition: Evidence from the United States
-
- Journal:
- Politics & Gender / Volume 21 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 220-245
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A review of the effectiveness of short-time work programmes: The Spanish case from a comparative perspective
-
- Journal:
- The Economic and Labour Relations Review / Volume 35 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 1000-1030
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
“Back to the Kitchen”: Corruption Charges Against Women Heads of Government–CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Political Science/Revue canadienne de science politique / Volume 57 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, p. 969
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Response to Shieh
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Philosophy / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 106-123
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
“A little world within itself”: The South Carolina Penitentiary and the Roots of the Carceral State
-
- Journal:
- Studies in American Political Development / Volume 38 / Issue 2 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 189-210
-
- Article
- Export citation
Framing the Judiciary: Effects of Partisan, Procedural, and Populist Frames on Apex Court Perceptions in Czechia
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Law and Courts / Volume 13 / Issue 1 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 97-121
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Limitarianism and Relative Thresholds
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Philosophy / Volume 54 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 43-58
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rethinking rebel victory in civil war
-
- Journal:
- Review of International Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 1-19
-
- Article
- Export citation
Access to healthcare for children with CHDs in middle and low-income countries: a systematic literature review
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 35 / Issue 3 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 482-489
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Case C-123/22, Comm'n v. Hung. (C.J.E.U.)
-
- Journal:
- International Legal Materials / Volume 64 / Issue 3 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 903-924
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Uchenna Okeja. Deliberative Agency: A Study in Modern African Political Philosophy. Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press, 2022. $30. Paper. ISBN: 9780253059918.
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 67 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 1085-1088
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Attitudes towards mental health professionals in social media: infodemiology study
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 227 / Issue 3 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 608-613
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Compact elements and the hypocompact radical of crossed products
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 68 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. 349-358
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Exploring Demographic Factors Influencing Indian Nursing Students’ Willingness to Volunteer
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 18 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, e324
-
- Article
- Export citation
Social Media Memes and Early Public Opinion Formation Regarding Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) as a Public Health Threat in the United States
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 19 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
CJN volume 51 issue 6 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2025, pp. f1-f6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation