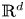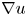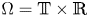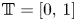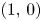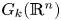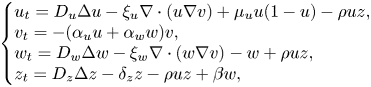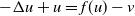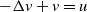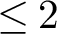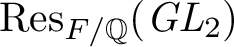Refine search
Actions for selected content:
25839 results in Abstract analysis
Absence of singularities in solutions for the compressible Euler equations with source terms in $\mathbb {R}^d$
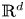
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 April 2022, pp. 978-1001
- Print publication:
- June 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stability and exponential decay for magnetohydrodynamic equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2022, pp. 853-880
- Print publication:
- June 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Steady state diffusion in tubular structures: Assessment of one-dimensional models
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2022, pp. 262-279
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Left regular representations of Garside categories I. C*-algebras and groupoids
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2022, pp. S53-S86
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Non-degeneracy of synchronized vector solutions for weakly coupled nonlinear schrödiner systems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 65 / Issue 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2022, pp. 441-459
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Atiyah–Patodi–Singer rho invariant and signatures of links
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 65 / Issue 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2022, pp. 404-440
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Corrigendum to “Topological complexity of real Grassmannians”
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2022, pp. 1071-1072
- Print publication:
- June 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The local cyclicity problem: Melnikov method using Lyapunov constants
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 65 / Issue 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2022, pp. 356-375
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the algebraicity about the Hodge numbers of the Hilbert schemes of algebraic surfaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 65 / Issue 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2022, pp. 392-403
-
- Article
- Export citation
Asymptotic behaviour in a doubly haptotactic cross-diffusion model for oncolytic virotherapy
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2022, pp. 881-906
- Print publication:
- June 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
A pinching estimate for convex hypersurfaces evolving under a non-homogeneous variant of mean curvature flow
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 65 / Issue 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2022, pp. 376-391
-
- Article
- Export citation
Homotopy commutativity in Hermitian symmetric spaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 64 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2022, pp. 746-752
-
- Article
- Export citation
Existence of solution for a class of activator–inhibitor systems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 65 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2022, pp. 98-113
-
- Article
- Export citation
A boson-fermion correspondence in cohomological Donaldson–Thomas theory
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2022, pp. S28-S52
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the Lie symmetries of characteristic function hierarchy in compressible turbulence
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 34 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2022, pp. 913-935
-
- Article
- Export citation
Analytic partial-integrability of a symmetric Hopf-zero degeneracy
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2022, pp. 833-852
- Print publication:
- June 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ON A PROPERNESS OF THE HILBERT EIGENVARIETY AT INTEGRAL WEIGHTS: THE CASE OF QUADRATIC RESIDUE FIELDS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 22 / Issue 6 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2022, pp. 2645-2716
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
GMJ volume 64 issue 2 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 64 / Issue 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 April 2022, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
JMJ volume 21 issue 3 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 21 / Issue 3 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 April 2022, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- May 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
JMJ volume 21 issue 3 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 21 / Issue 3 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 April 2022, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- May 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation