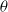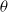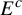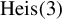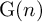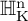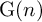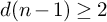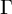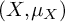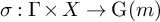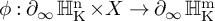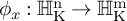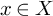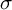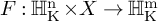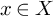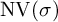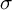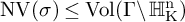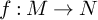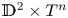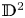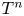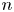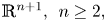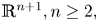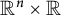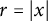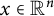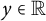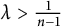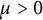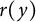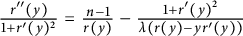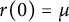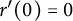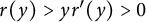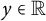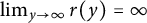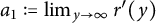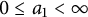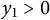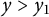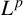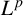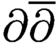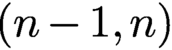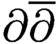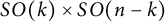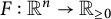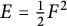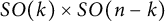Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
491 results in 53Cxx
On point processes defined by angular conditions on Delaunay neighbors in the Poisson–Voronoi Tessellation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 58 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. 952-965
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Partially hyperbolic diffeomorphisms and Lagrangian contact structures
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 42 / Issue 8 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 November 2021, pp. 2583-2629
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
PL DENSITY INVARIANT FOR TYPE II DEGENERATING K3 SURFACES, MODULI COMPACTIFICATION AND HYPER-KÄHLER METRIC
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Nagoya Mathematical Journal / Volume 247 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2021, pp. 574-614
-
- Article
- Export citation
Anisotropic Gauss curvature flows and their associated Dual Orlicz-Minkowski problems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 November 2021, pp. 148-162
- Print publication:
- February 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Topological volumes of fibrations: a note on open covers
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 October 2021, pp. 1340-1360
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Defining relations of quantum symmetric pair coideal subalgebras
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 9 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2021, e67
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
NATURAL MAPS FOR MEASURABLE COCYCLES OF COMPACT HYPERBOLIC MANIFOLDS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 22 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2021, pp. 421-448
- Print publication:
- January 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
MANY FINITE-DIMENSIONAL LIFTING BUNDLE GERBES ARE TORSION
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 105 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 September 2021, pp. 323-338
- Print publication:
- April 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Riemannian approximation in Carnot groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2021, pp. 1139-1154
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Discs area-minimizing in mean convex Riemannian n-manifolds
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2021, pp. 1361-1382
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
On regular algebraic hypersurfaces with non-zero constant mean curvature in Euclidean spaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 4 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2021, pp. 1081-1088
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Counting closed geodesics in a compact rank-one locally CAT(0) space
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 42 / Issue 3 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2021, pp. 1220-1251
- Print publication:
- March 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Unique continuation properties for polyharmonic maps between Riemannian manifolds
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 75 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2021, pp. 1-28
- Print publication:
- February 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cyclic parallel structure Jacobi operator for real hypersurfaces in complex two-plane Grassmannians
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 4 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 August 2021, pp. 939-964
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Counting and equidistribution in quaternionic Heisenberg groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society / Volume 173 / Issue 1 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 July 2021, pp. 67-104
- Print publication:
- July 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nontame Morse–Smale flows and odd Chern–Weil theory
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 74 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 July 2021, pp. 1579-1624
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Existence of hypercylinder expanders of the inverse mean curvature flow
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 65 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2021, pp. 543-551
- Print publication:
- September 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
SOME
 $\boldsymbol {L^p}$-HARDY AND
$\boldsymbol {L^p}$-HARDY AND  $\boldsymbol {L^p}$-RELLICH TYPE INEQUALITIES WITH REMAINDER TERMS
$\boldsymbol {L^p}$-RELLICH TYPE INEQUALITIES WITH REMAINDER TERMS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 113 / Issue 1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 June 2021, pp. 79-98
-
- Article
- Export citation
POWER SERIES PROOFS FOR LOCAL STABILITIES OF KÄHLER AND BALANCED STRUCTURES WITH MILD
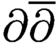 $\partial \overline {\partial }$-LEMMA
$\partial \overline {\partial }$-LEMMA
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Nagoya Mathematical Journal / Volume 246 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 June 2021, pp. 305-354
-
- Article
- Export citation
Proof of Laugwitz Conjecture and Landsberg Unicorn Conjecture for Minkowski norms with
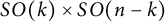 $SO(k)\times SO(n-k)$-symmetry
$SO(k)\times SO(n-k)$-symmetry
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 74 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2021, pp. 1486-1516
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation