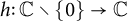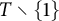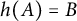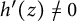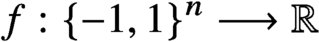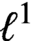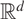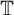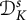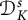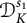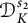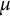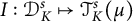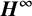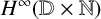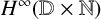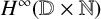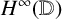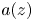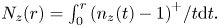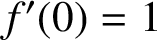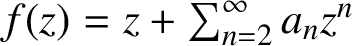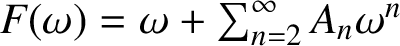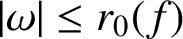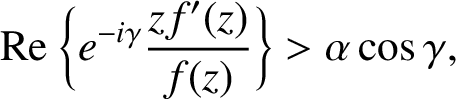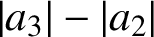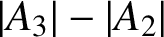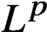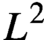Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
543 results in 30xxx
Analytic order-isomorphisms of countable dense subsets of the unit circle
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 65 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2021, pp. 653-664
- Print publication:
- September 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dual exponential polynomials and a problem of Ozawa
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 June 2021, pp. 701-719
- Print publication:
- June 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
More on zeros and approximation of the Ising partition function
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 9 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 June 2021, e46
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Permutable quasiregular maps
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society / Volume 173 / Issue 1 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2021, pp. 105-121
- Print publication:
- July 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Une note sur la densité des zéros des sommes partielles de la fonction zeta de Dedekind sur un corps quadratique
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 65 / Issue 2 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2021, pp. 409-415
- Print publication:
- June 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Asymptotic first boundary value problem for holomorphic functions of several complex variables
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 65 / Issue 2 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2021, pp. 361-380
- Print publication:
- June 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Characterizations of Morrey type spaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 65 / Issue 2 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 May 2021, pp. 328-344
- Print publication:
- June 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
DENSE STABLE RANK AND RUNGE-TYPE APPROXIMATION THEOREMS FOR
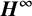 ${\boldsymbol H}^{\boldsymbol{\infty}}$ MAPS
${\boldsymbol H}^{\boldsymbol{\infty}}$ MAPS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 113 / Issue 3 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 May 2021, pp. 289-317
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Geometric series expansion of the Neumann–Poincaré operator: Application to composite materials
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 33 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2021, pp. 560-585
-
- Article
- Export citation
Peaking and interpolation by complex polynomials
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 64 / Issue 2 / May 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 May 2021, pp. 129-138
-
- Article
- Export citation
On non-separated zero sequences of solutions of a linear differential equation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 64 / Issue 2 / May 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 April 2021, pp. 247-261
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the dimension of points which escape to infinity at given rate under exponential iteration
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 42 / Issue 5 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 March 2021, pp. 1591-1623
- Print publication:
- May 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
CARLESON INTERPOLATING SEQUENCES FOR BANACH SPACES OF ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 21 / Issue 6 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 March 2021, pp. 1915-1945
- Print publication:
- November 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
A NOTE ON SPIRALLIKE FUNCTIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 105 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2021, pp. 117-123
- Print publication:
- February 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Unitary equivalence of multiplication operators on the Bergman spaces of polygons
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 65 / Issue 1 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2021, pp. 123-133
- Print publication:
- March 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Orbifold expansion and entire functions with bounded Fatou components
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 42 / Issue 5 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 March 2021, pp. 1807-1846
- Print publication:
- May 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Global boundedness of a class of multilinear Fourier integral operators
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 9 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 February 2021, e14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Characterizations of Hankel operators in the essential commutant of quasicontinuous Toeplitz operators
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 65 / Issue 1 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 February 2021, pp. 44-51
- Print publication:
- March 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
On Ruelle’s property
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 42 / Issue 4 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2021, pp. 1474-1486
- Print publication:
- April 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Vortices over Riemann surfaces and dominated splittings
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 42 / Issue 5 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2021, pp. 1781-1806
- Print publication:
- May 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation