Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
300 results in 47Axx
U-Operators
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 78 / Issue 1 / February 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 59-90
- Print publication:
- February 2005
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The eigentime identity for continuous-time ergodic Markov chains
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 41 / Issue 4 / December 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2016, pp. 1071-1080
- Print publication:
- December 2004
-
- Article
- Export citation
On quasinilpotent Operators, II
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 77 / Issue 3 / December 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 349-356
- Print publication:
- December 2004
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Operator-valued multiplier theorems characterizing Hilbert spaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 77 / Issue 2 / October 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 175-184
- Print publication:
- October 2004
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Ergodicity and stability of orbits of unbounded semigroup representations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 77 / Issue 2 / October 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 209-232
- Print publication:
- October 2004
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Random dynamical systems with jumps
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 41 / Issue 3 / September 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2016, pp. 890-910
- Print publication:
- September 2004
-
- Article
- Export citation
Relatively compact-like perturbations, essential spectra and application
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 77 / Issue 1 / August 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 73-90
- Print publication:
- August 2004
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Infinite- and finite-buffer Markov fluid queues: a unified analysis
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 41 / Issue 2 / June 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2016, pp. 557-569
- Print publication:
- June 2004
-
- Article
- Export citation
The generalized condition numbers of bounded linear operators in Banach spaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 76 / Issue 2 / April 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 281-290
- Print publication:
- April 2004
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Generalized Weyl's theorem and hyponormal operators
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 76 / Issue 2 / April 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 291-302
- Print publication:
- April 2004
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Homogeneous quasi-invariant subspaces of the fock space
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 75 / Issue 3 / December 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 399-408
- Print publication:
- December 2003
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
An extension of Henrici theorem for the joint approximate spectrum of commuting spectral operators
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 75 / Issue 2 / October 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 233-246
- Print publication:
- October 2003
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Lacunas in the Support of the Weyl Calculus for Two Hermitian Matrices
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 75 / Issue 1 / August 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 85-124
- Print publication:
- August 2003
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Two Results About H∞ Functional Calculus on Analytic umd Banach Spaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 74 / Issue 3 / June 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 351-378
- Print publication:
- June 2003
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Additive results for the generalized Drazin inverse
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 73 / Issue 1 / August 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 115-126
- Print publication:
- August 2002
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The perturbation theory for the Drazin inverse and its applications II
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 70 / Issue 2 / April 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 189-198
- Print publication:
- April 2001
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Essentially commutative C*-algebras with essential spectrum homeomorphic to S2n−1
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 70 / Issue 2 / April 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 199-210
- Print publication:
- April 2001
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Compactness properties for perturbed semigroups and application to transport equation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 69 / Issue 1 / August 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 25-40
- Print publication:
- August 2000
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Spectral and asymptotic properties of resolvent-dominated operators
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society. Series A. Pure Mathematics and Statistics / Volume 68 / Issue 2 / April 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 April 2009, pp. 181-201
- Print publication:
- April 2000
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The fundamental matrix of singularly perturbed Markov chains
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 31 / Issue 3 / September 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2016, pp. 679-697
- Print publication:
- September 1999
-
- Article
- Export citation
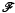 , the reduced Beurling spectrum of ø is empty if and only if ø ∈
, the reduced Beurling spectrum of ø is empty if and only if ø ∈