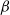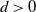Refine search
Actions for selected content:
52664 results in Statistics and Probability
Performance and accuracy assessments of an incompressible fluid solver coupled with a deep convolutional neural network—ADDENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Data-Centric Engineering / Volume 3 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 April 2022, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Data trust and data privacy in the COVID-19 period—ADDENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Data & Policy / Volume 4 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 April 2022, e10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
MCMC for a hyperbolic Bayesian inverse problem in traffic flow modelling – ADDENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Data-Centric Engineering / Volume 3 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 April 2022, e8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
DERGMs: Degeneracy-restricted exponential family random graph models
-
- Journal:
- Network Science / Volume 10 / Issue 1 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 March 2022, pp. 82-110
-
- Article
- Export citation
Joint moments of discounted claims and discounted perturbation until ruin in the compound Poisson risk model with diffusion
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 37 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 March 2022, pp. 387-417
-
- Article
- Export citation
The stochastic actor-oriented model is a theory as much as it is a method and must be subject to theory tests
-
- Journal:
- Network Science / Volume 10 / Issue 1 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 March 2022, pp. 15-19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
CALIBRATING THE LEE-CARTER AND THE POISSON LEE-CARTER MODELS VIA NEURAL NETWORKS
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA / Volume 52 / Issue 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 March 2022, pp. 519-561
- Print publication:
- May 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
An explicit Dobrushin uniqueness region for Gibbs point processes with repulsive interactions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 59 / Issue 2 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2022, pp. 541-555
- Print publication:
- June 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Identified risk factors for co-infection in hospitalised children infected with adenovirus in Hangzhou
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2022, e80
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Optimal discounted drawdowns in a diffusion approximation under proportional reinsurance
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 59 / Issue 2 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2022, pp. 527-540
- Print publication:
- June 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Climate scenario analysis: An illustration of potential long-term economic & financial market impacts
-
- Journal:
- British Actuarial Journal / Volume 27 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2022, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Climate scenario analysis for pension schemes: a UK case study
-
- Journal:
- British Actuarial Journal / Volume 27 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 March 2022, e6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The application framework of big data technology during the COVID-19 pandemic in China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 March 2022, e71
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Statistical analysis between 2006 and 2019 and forecast of rabies in cattle from 2020 to 2022 in Tocantins State (Brazil), by using the R Studio software
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 March 2022, e82
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An averaging process on hypergraphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 59 / Issue 2 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 March 2022, pp. 495-504
- Print publication:
- June 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Public health implications of plasmid-mediated quinolone and aminoglycoside resistance genes in Escherichia coli inhabiting a major anthropogenic river of India
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 March 2022, e78
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
SIMULTANEOUS EQUATIONS MODELS WITH HIGHER-ORDER SPATIAL OR SOCIAL NETWORK INTERACTIONS
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 39 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 March 2022, pp. 1154-1201
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
INFERENCE ON THE DIMENSION OF THE NONSTATIONARY SUBSPACE IN FUNCTIONAL TIME SERIES
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 39 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 March 2022, pp. 443-480
-
- Article
- Export citation
ON MULTIPLE STRUCTURAL BREAKS IN DISTRIBUTION: AN EMPIRICAL CHARACTERISTIC FUNCTION APPROACH
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 39 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2022, pp. 534-581
-
- Article
- Export citation
Principal component density estimation for scenario generation using normalizing flows
-
- Journal:
- Data-Centric Engineering / Volume 3 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2022, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation