Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1382931 results in Open Access
Alternative to Ontology or Alternative Ontology? Allison on the ‘Proud Name’ of Ontology (A247/B303)
-
- Journal:
- Kantian Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 December 2025, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Design and analysis of a circularly polarized Nabla-slotted waveguide antenna for reflector application
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 December 2025, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Predicting and comparative soil quality assessment in organic and conventional hazelnut orchards using XGBoost approach
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 164 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 December 2025, e9
-
- Article
- Export citation
The association between intake of main flavonoid classes and menopausal age: a population-based and cross-sectional study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 135 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 December 2025, pp. 435-447
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2026
-
- Article
- Export citation
Aging-in-Place (Vieillir Chez Soi, VCS) in a Seniors’ Residence: Co-Development, Implementation, and Evaluation of a Care Approach to Delay Transitions in Long-Term Care
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement / Volume 45 / Issue 1 / March 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 December 2025, pp. 131-141
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Health data justice, epistemological delinking and vernacularisation: reclaiming knowledge, rights and representation
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Law in Context / Volume 22 / Issue 1 / March 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 December 2025, pp. 75-89
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
EuMW 2024 special issue
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 17 / Issue 9 / November 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 December 2025, p. 1443
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Marangoni-driven freezing dynamics of supercooled binary droplets
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1026 / 10 January 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 December 2025, A11
-
- Article
- Export citation
A point vortex model for spike-type instability leading to rotating stall
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1026 / 10 January 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 December 2025, A1
-
- Article
- Export citation
Sources of madness: investigating the post-colonial history of psychiatry in Niger
-
- Journal:
- Medical History , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 December 2025, pp. 1-19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
V.Y. Mudimbe: On Invention, Odor, and Toxicity
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 68 / Issue 4 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 December 2025, pp. 862-866
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
PDJ volume 40 issue 4 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 40 / Issue 4 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 December 2025, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
MAXIMAL
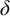 $\delta $-SEPARATED SETS IN SEPARABLE METRIC SPACES AND WEAK FORMS OF CHOICE
$\delta $-SEPARATED SETS IN SEPARABLE METRIC SPACES AND WEAK FORMS OF CHOICE
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Symbolic Logic , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 December 2025, pp. 1-15
-
- Article
- Export citation
Biological attributes, predatory potential and functional response of syrphid, Episyrphus viridaureus (Weidemann) on potato aphid, Macrosiphum euphorbiae (Thomas) infesting tomato
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 December 2025, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Fluctuation–dissipation theorems in porous media two-phase flow: statistical characterisation of saturation fluctuations and measurement of Onsager coefficients
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1026 / 10 January 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 December 2025, A2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Crystal structure of valganciclovir hydrochloride, C14H23N6O5Cl
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 40 / Issue 4 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 December 2025, pp. 304-312
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Is the Knowledge Argument a Frege Puzzle?
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Philosophy / Volume 55 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 December 2025, pp. 99-115
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
THE ALGEBRAS OF LEWIS’S COUNTERFACTUALS: DUALITY THEORY
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Review of Symbolic Logic / Volume 19 / Issue 1 / March 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 December 2025, pp. 46-80
- Print publication:
- March 2026
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nutrition in early life, epigenetics and lifelong health – evidence from cohort and intervention studies
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 December 2025, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
FROM BUST TO BOTTLENECKS: LESSONS FROM THE IRISH EXPERIENCE OF PUBLIC INVESTMENT AND FISCAL POLICY
-
- Journal:
- National Institute Economic Review ,
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 December 2025, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation