Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1416487 results in Open Access
Notes on Contributors
-
- Journal:
- Contemporary European History / Volume 33 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 379-382
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Economic Sanctions and the Material Well-being of Iranian Older Adults: Do Pensions Make a Difference?
-
- Journal:
- Social Policy and Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
James Hannam, The Globe: How the Earth Became Round London: Reaktion Books, 2023. Pp. 376. ISBN 978-1-78914-758-2. £16.99 (hardback).
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal for the History of Science / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 311-312
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Construction and Government of Lunatic Asylums and Hospitals for the Insane, by John Conolly
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Advances / Volume 30 / Issue 4 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 257-261
- Print publication:
- July 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Racial Colonists in the Nazi East: Disabled Veterans and the Malleable Boundaries of Race, Masculinity, and Disability
-
- Journal:
- Central European History / Volume 57 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 59-77
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Precedential Value of Judicial Decisions in Increasingly Hybridised Civil Law Systems: Chinese Choreographies at the WTO
-
- Journal:
- Asian Journal of Comparative Law / Volume 19 / Issue 1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 107-141
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Alcohol Use Disorder in Patients with Chronic Migraine: A Retrospective, Observational Study
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 767-777
-
- Article
- Export citation
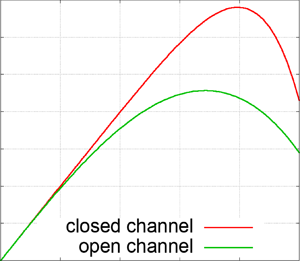
The open channel in a uniform representation of the turbulent velocity profile across all parallel geometries
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, R1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Assessment of perinatal anxiety: diagnostic accuracy of five measures
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 224 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 132-138
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Paternalism, petitions and the politics of church construction in Alsace, c. 1850–1885
-
- Journal:
- Urban History / Volume 51 / Issue 4 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 793-809
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Lethal effect of Goniozus legneri on Cactoblastis cactorum: A potential biocontrol agent for inundative releases
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 149-158
-
- Article
- Export citation
BAZ volume 109 issue 1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 109 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Delivery of a telehealth supported home exercise program with dietary advice to increase plant-based protein intake in people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a 12-week randomised controlled feasibility trial
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 10 / 28 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 1709-1719
- Print publication:
- 28 May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Anxiety in late-life depression: Associations with brain volume, amyloid beta, white matter lesions, cognition, and functional ability
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 36 / Issue 11 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 1009-1020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dynamic interaction of gravity currents in a confined porous layer
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, A52
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Notion of Heresy in Greek Literature in the Second and Third Centuries By Alain Le Boulluec, edited by David Lincicum and Nicholas Moore, translated by A.K.M. Adam, Monique Cuany, Nicholas Moore, Warren Campbell, and Jordan Daniel Wood, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2022, pp. 736, £150.00, hbk
-
- Journal:
- New Blackfriars / Volume 105 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 200-202
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
A five-year quasi-experimental study to evaluate the impact of empiric antibiotic order sets on antibiotic use metrics among hospitalized adult patients
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 609-617
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Who Gets Hired? Political Patronage and Bureaucratic Favoritism
-
- Journal:
- American Political Science Review / Volume 118 / Issue 4 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 1913-1930
- Print publication:
- November 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Gunnar Broberg, The Man Who Organized Nature: The Life of Linnaeus Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2023. Pp. 512. ISBN 978-0-691-21342-2. £35.00 (hardcover).
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal for the History of Science / Volume 57 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 497-499
- Print publication:
- September 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Implementing a continuous quality-improvement framework for tuberculosis infection prevention and control in healthcare facilities in China, 2017–2019
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 651-657
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation