Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419634 results in Open Access
Retrospective Analysis of Canadian Adults with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue 5 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 636-643
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
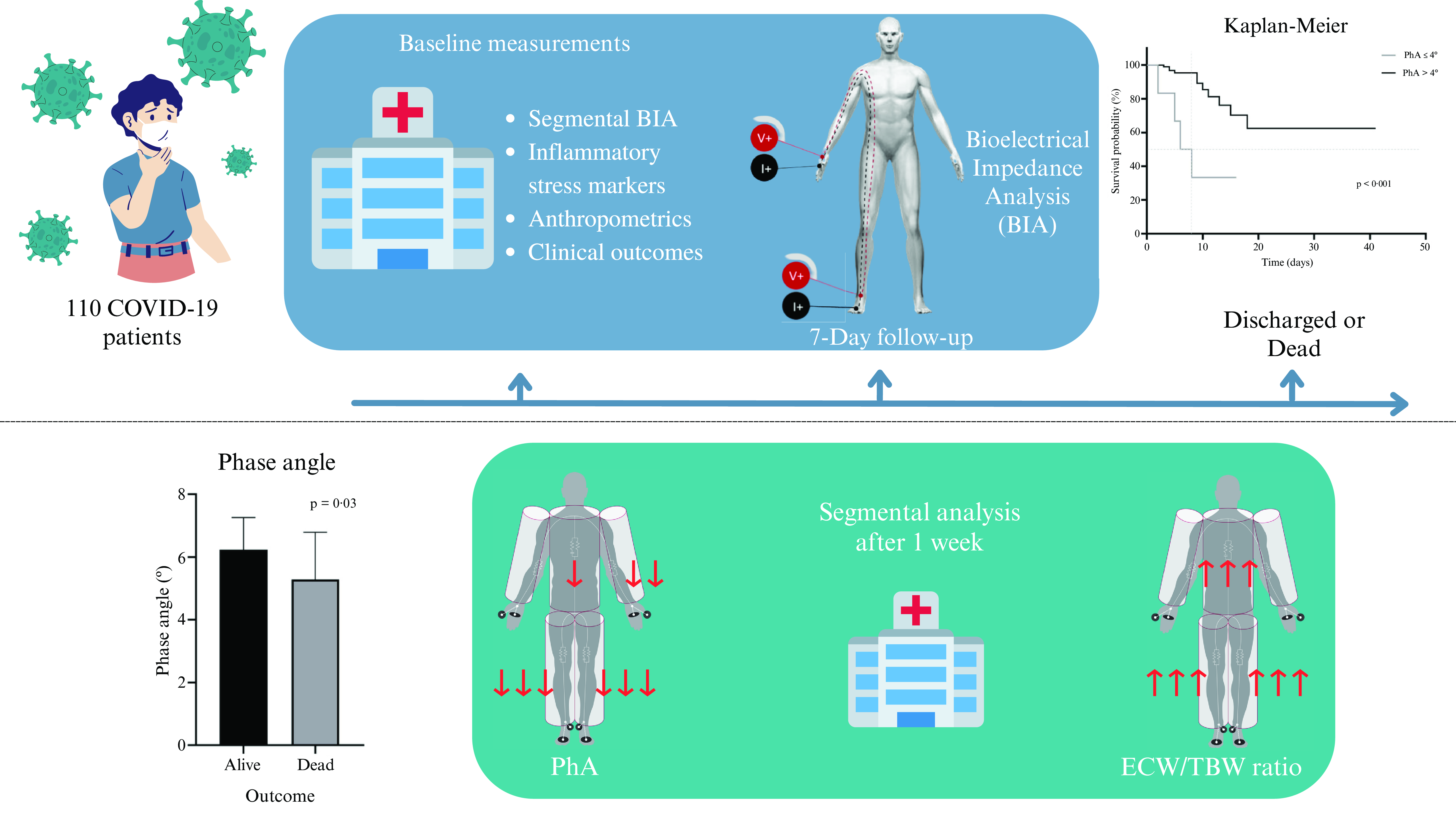
Total and segmental phase angle in a cohort of hospitalised patients with COVID-19: mortality prediction and changes throughout hospitalisation
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 1397-1404
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
COUNTING UNIONS OF SCHREIER SETS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 110 / Issue 1 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 19-31
- Print publication:
- August 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
A revised gap-averaged Floquet analysis of Faraday waves in Hele-Shaw cells
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 977 / 25 December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, A45
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Oswaldocruzia franciscoensis n. sp. (Nematoda: Molineidae) in Leptodactylus macrosternum Miranda-Ribeiro, 1926 (Anura: Leptodactylidae) from Caatinga morphoclimatic domain, Brazil: morphological and molecular characterisation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 97 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, e104
-
- Article
- Export citation
Inertial range scaling of inhomogeneous turbulence
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 978 / 10 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, A9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Granular dilatancy and non-local fluidity of partially molten rock
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 978 / 10 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, A7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Bridging the Blue Divide: The Democrats’ New Metro Coalition and the Unexpected Prominence of Redistribution
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 609-629
- Print publication:
- September 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Objective Structured Clinical Examination: Underused Tool in Epilepsy Fellowship Programs?
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 865-867
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Headache Education in Canadian Medical Schools
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 845-847
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Response by Conrad C. Labandeira for the presentation of the 2022 Paleontological Society Medal
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 97 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 1157-1158
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
How do proactive career behaviors translate into subjective career success and perceived employability? The role of thriving at work and humble leadership
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Management & Organization / Volume 30 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 2088-2104
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Prospective Post-Marketing Observational Study of Brivaracetam in People With Focal Epilepsy
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 860-864
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Self-propulsion of an elliptical phoretic disk emitting solute uniformly – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 977 / 25 December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, E1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Stew in silence or boil up gradually? A process model of employees’ remedial voice
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Management & Organization / Volume 30 / Issue 5 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 1607-1621
-
- Article
- Export citation
Vorticity dynamics in transcritical liquid jet breakup
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 978 / 10 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, A6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dynamics of the interaction of a pair of thin evaporating droplets on compliant substrates
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 978 / 10 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, A8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Gendered Institutions and Where to Find Them: A Critical Realist Approach
-
- Journal:
- Politics & Gender / Volume 20 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 449-473
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation