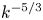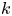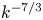Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419606 results in Open Access
Loess transportation surfaces in west-central Wisconsin, USA
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 120 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 36-52
-
- Article
- Export citation
The role of viscoplastic drop shape in impact
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 978 / 10 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, A1
-
- Article
- Export citation
SOLVABLE GROUPS WHOSE NONNORMAL SUBGROUPS HAVE FEW ORDERS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 110 / Issue 1 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 121-128
- Print publication:
- August 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Scientizing the ‘environment’: Solly Zuckerman and the idea of the School of Environmental Sciences
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal for the History of Science / Volume 57 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 99-112
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Imbibition and collapse between swelling fibres
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 978 / 10 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, A2
-
- Article
- Export citation
The rolling snowball: lone English-origin lexical items in Guernésiais
-
- Journal:
- Journal of French Language Studies / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 155-179
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Meridional rank and bridge number of knotted 2-spheres
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 77 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 282-299
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
LATE ROMAN FIELD ARMIES - (A.) Kaldellis, (M.) Kruse The Field Armies of the East Roman Empire, 361–630. Pp. xxii + 205, maps. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2023. Cased, £85, US$110. ISBN: 978-1-009-29694-6.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 74 / Issue 1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 212-214
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Currency Carry, Momentum, and Global Interest Rate Volatility
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis / Volume 60 / Issue 2 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 839-873
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Vapaki: Ancestral O'Odham Platform Mounds of the Sonoran Desert. Glen E. Rice, Arleyn W. Simon, and Chris Loendorf, editors. 2023. University of Utah Press, Salt Lake City. xx + 305 pp. $80.00 (hardcover), ISBN 978-1-64769-117-2. $64.00 (e-book), ISBN 978-1-64769-119-6.
-
- Journal:
- American Antiquity / Volume 89 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 328-330
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Should pediatric cardiologists refer all patients with unexplained chest pain to a psychiatrist?
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 6 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 1211-1217
-
- Article
- Export citation
Retrospective Analysis of Canadian Adults with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue 5 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 636-643
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
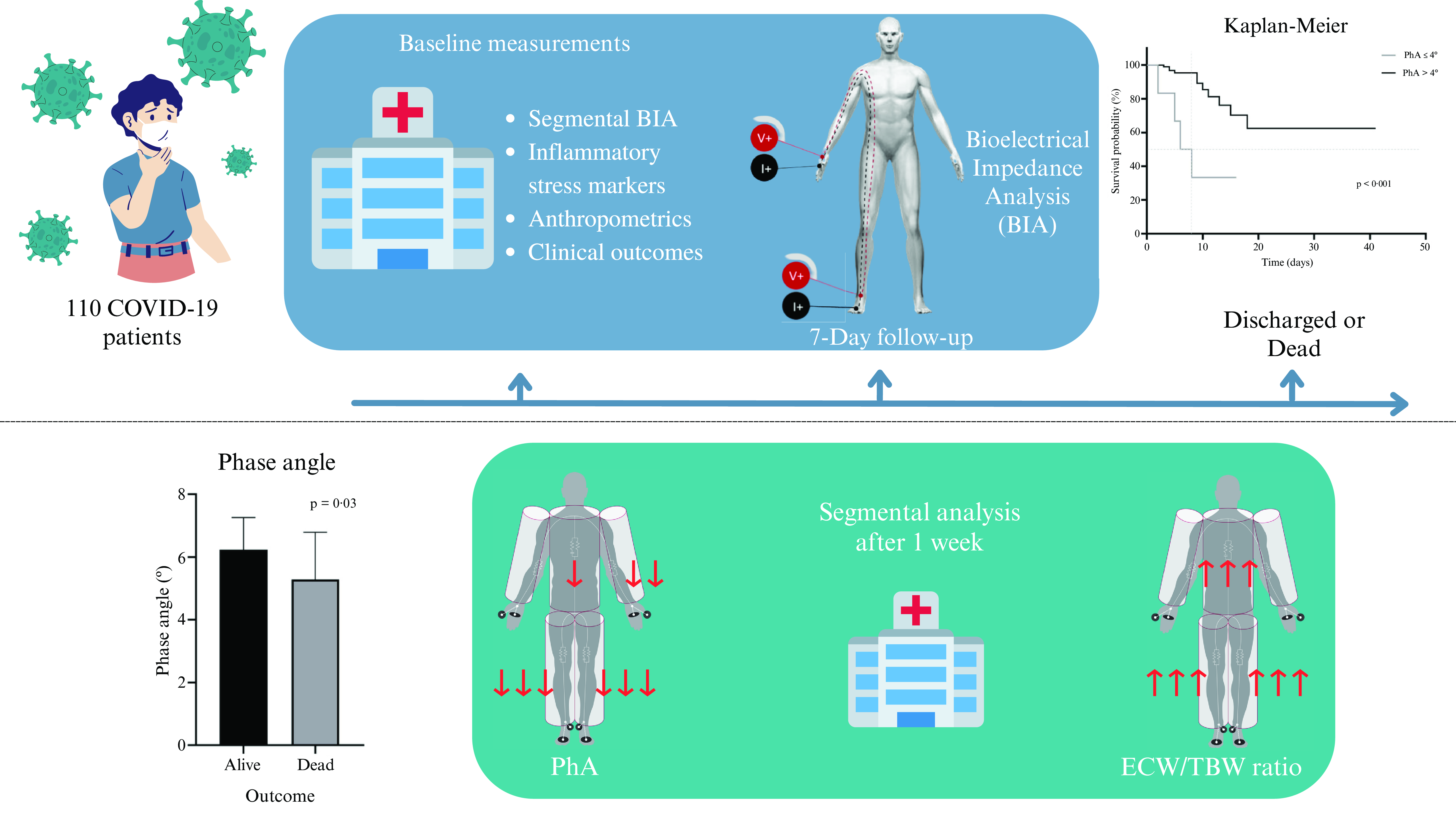
Total and segmental phase angle in a cohort of hospitalised patients with COVID-19: mortality prediction and changes throughout hospitalisation
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 1397-1404
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
COUNTING UNIONS OF SCHREIER SETS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 110 / Issue 1 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, pp. 19-31
- Print publication:
- August 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
A revised gap-averaged Floquet analysis of Faraday waves in Hele-Shaw cells
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 977 / 25 December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, A45
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Oswaldocruzia franciscoensis n. sp. (Nematoda: Molineidae) in Leptodactylus macrosternum Miranda-Ribeiro, 1926 (Anura: Leptodactylidae) from Caatinga morphoclimatic domain, Brazil: morphological and molecular characterisation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 97 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, e104
-
- Article
- Export citation
Inertial range scaling of inhomogeneous turbulence
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 978 / 10 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, A9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Granular dilatancy and non-local fluidity of partially molten rock
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 978 / 10 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2023, A7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation