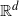Refine search
Actions for selected content:
52651 results in Statistics and Probability
Bayesian parameter inference for shallow subsurface modeling using field data and impacts on geothermal planning
-
- Journal:
- Data-Centric Engineering / Volume 3 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2022, e32
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Geographical distribution and space–time clustering of human illnesses with major Salmonella serotypes in Florida, USA, 2017–2018
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2022, e175
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Optimal design for network mutual aid
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 37 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2022, pp. 567-596
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
An outbreak of Cryptosporidium parvum linked to pasteurised milk from a vending machine in England: a descriptive study, March 2021
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2022, e185
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
REGULARIZED ESTIMATION OF DYNAMIC PANEL MODELS
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 40 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2022, pp. 360-418
-
- Article
- Export citation
On stochastic ordering among extreme shock models
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 37 / Issue 4 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2022, pp. 961-972
-
- Article
- Export citation
SUPERCONSISTENCY OF TESTS IN HIGH DIMENSIONS
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 40 / Issue 3 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2022, pp. 688-704
-
- Article
- Export citation
TESTING FOR STRICT STATIONARITY VIA THE DISCRETE FOURIER TRANSFORM
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 40 / Issue 3 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2022, pp. 511-557
-
- Article
- Export citation
TESTING FOR HOMOGENEOUS THRESHOLDS IN THRESHOLD REGRESSION MODELS
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 40 / Issue 3 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2022, pp. 608-651
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A negative binomial approximation in group testing
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 37 / Issue 4 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2022, pp. 973-996
-
- Article
- Export citation
Spillover benefit of pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention: evaluating the importance of effect modification using an agent-based model
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2022, e192
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A MOLLIFIER APPROACH TO THE DECONVOLUTION OF PROBABILITY DENSITIES
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 40 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2022, pp. 320-359
-
- Article
- Export citation
Bose–Einstein condensation for particles with repulsive short-range pair interactions in a Poisson random external potential in
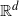 $\mathbb{R}^{d}$
$\mathbb{R}^{d}$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 60 / Issue 2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2022, pp. 382-393
- Print publication:
- June 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prevalence and surveillance of tuberculosis in Yemen from 2006 to 2018 – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2022, e174
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
1 - Introduction
-
- Book:
- Large Deviations for Markov Chains
- Published online:
- 03 August 2022
- Print publication:
- 27 October 2022, pp 1-13
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
7 - Upper Bounds III: Sufficient Conditions
-
- Book:
- Large Deviations for Markov Chains
- Published online:
- 03 August 2022
- Print publication:
- 27 October 2022, pp 94-116
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Appendix B - Irreducible Kernels, Small Sets, and Petite Sets
-
- Book:
- Large Deviations for Markov Chains
- Published online:
- 03 August 2022
- Print publication:
- 27 October 2022, pp 200-211
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
8 - The Large Deviation Principle for Empirical Measures
-
- Book:
- Large Deviations for Markov Chains
- Published online:
- 03 August 2022
- Print publication:
- 27 October 2022, pp 117-133
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Appendix E - On Varadhan’s Theorem
-
- Book:
- Large Deviations for Markov Chains
- Published online:
- 03 August 2022
- Print publication:
- 27 October 2022, pp 223-226
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Appendix A - The Ergodic Theorem for Empirical Measures and Vector-Valued Functionals of a Markov Chain
-
- Book:
- Large Deviations for Markov Chains
- Published online:
- 03 August 2022
- Print publication:
- 27 October 2022, pp 197-199
-
- Chapter
- Export citation