Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
2107743 results in Journals
Teaching additional languages to young learners through tasks
-
- Journal:
- Language Teaching , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ASKAP discovery of a 30 kpc bipolar outflow from the edge-on disk of the nearby spiral galaxy ESO 130-G012
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
CCC volume 58 issue 4 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Central European History / Volume 58 / Issue 4 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Rotations in
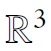 $\mathbb{R}^3$ and
$\mathbb{R}^3$ and  $\mathbb{R}^4$
$\mathbb{R}^4$
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
THE HISTORY OF SARCOPHAGI IN THE IBERIAN PENINSULA - Begoña Torre Miguel, Teoría y práctica del spolium. Los sarcófagos de la Antigüedad reutilizados en los reinos cristianos medievales de la Península Ibérica. (Iberia Selecta 4.) Pp. 352, b/w & colour ills, colour map. Stuttgart: Franz Steiner, 2025. Cased, €68. ISBN: 978-3-515-13529-0.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
VISUALISING THE INVISIBLE - Carolyn Laferrière, Divine Music in Archaic and Classical Greek Art. Seeing the Songs of the Gods. Pp. xx + 282, b/w & colour ills. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2024. Cased, £85, US$110. ISBN: 978-1-009-31594-4.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
Flow over a cylinder with a small triangular bump
-
- Journal:
- Flow: Applications of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 6 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, E5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chinese Multinational Enterprises in a New Reality: Advancing International Business Theory
-
- Journal:
- Management and Organization Review / Volume 21 / Issue 6 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1034-1052
-
- Article
- Export citation
The politics behind political science: A cross-national perspective
-
- Journal:
- European Political Science ,
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Strengthening Health Technology Assessment (HTA) in the European Union: Insights from Slovenia’s Implementation Journey
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Invisible design and acoustic scattering of metamaterial plates with active feedback control
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1029 / 25 February 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, A25
-
- Article
- Export citation
Real Disinvestments and the Distress Anomaly: Evidence from Stocks, Bonds, and Loans
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-77
-
- Article
- Export citation
UAV tracking one moving target in an oilfield environment with dynamic obstacles based on an improved salp swarm algorithm
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-21
-
- Article
- Export citation
Radiotherapy clinical placement: a perspective from culturally and linguistically diverse students in the UK
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Radiotherapy in Practice / Volume 25 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Gender and the Reelection of Democratic Leaders
-
- Journal:
- Politics & Gender , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Attitude stability control system for a hexapod bionic robot under hybrid disturbances
-
- Journal:
- Robotica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
- Export citation
Plant-based analogues to meat and dairy for sustainable food systems
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-38
-
- Article
- Export citation
FUTURES PAST
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Xenomusicology
-
- Journal:
- Organised Sound , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
South American Encounters with the Orient, 1893–1897: Ultramontanism, Modernity and Prophetism
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Ecclesiastical History , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation