Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
2107743 results in Journals
Male Agency? Analyzing Fatherhood Roles in Swedish Parliamentary Documents, 1993–2021
-
- Journal:
- Politics & Gender , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-30
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
‘Friendshoring’ the seabed: Securing submarine cables through network centrality
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of International Security , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Sleep State is Superior to Resting State for Heart Rate Variability Assessment in Major Depressive Disorder
-
- Journal:
- Acta Neuropsychiatrica / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Network models of symptoms following mild traumatic brain injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
APOLLONIUS RHODIUS AND ‘HOMER’ - Brian D. McPhee, Apollonius’ Argonautica and the Homeric Hymns. A Study in Hymnody, Hero Cult, and Homeric Reception. (Mnemosyne Supplements 489.) Pp. xiv + 441. Leiden and Boston: Brill, 2025. Cased, €150. ISBN: 978-90-04-71510-3.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
Jan Turek & Petr Krištuf 2025. The tombs of forefathers: Neolithic long barrows in ritual landscapes. Oxford: Oxbow; 979-8-88857-202-3 paperback £42.
-
- Journal:
- Antiquity , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
Complete regularity of linear cocycles and the Baire category of the set of Lyapunov-Perron regular points
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 14 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
MORE RESEARCH ON GALEN - P. N. Singer / Ralph M. Rosen (edd.), The Oxford Handbook of Galen. Pp. xxii + 736, ills, maps. New York: Oxford University Press, 2024. Cased, £115, US$150. ISBN: 978-0-19-091368-7.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Perceptions of Feminism as a Threat
-
- Journal:
- Politics & Gender , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Indian Coffee House Workers Movement, 1936–1977: From Colonial Firm to Workers Cooperative
-
- Journal:
- International Labor and Working-Class History , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Must One Indeed Imagine Sisyphus Happy? Recurring Judicial Accountability Rounds as Rule of Law Exceptions in Post-Communist Europe
-
- Journal:
- German Law Journal ,
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The role of negative affectivity in the developmental pathway linking perinatal complications to behavioral and emotional problems in children
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Triage and System Gaps Observed During a 2025 Mass-Casualty Incident in Sanxia, Taiwan: A Report from the Field
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 20 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, e44
-
- Article
- Export citation
Letter from the Editor
-
- Journal:
- Management and Organization Review / Volume 21 / Issue 6 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, p. 1033
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Glyphosate Resistance in Italian ryegrass (Lolium perenne ssp. multiflorum) from New York State Associated with EPSPS Gene Amplification
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
ORDINAL DEFINABILITY IN
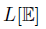 $L\left[\mathbb{E}\right]$
$L\left[\mathbb{E}\right]$
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Symbolic Logic / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-49
-
- Article
- Export citation
Rethinking Schizophrenia: Optimizing Care Pathways in Europe from the First Episode of Psychosis to Long-Term Care
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Alternatives to Glyphosate for Spring Preplant Foliar Weed Management
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The National Alliance for Radiation Readiness (NARR): Driving Partnerships Within the Radiation Readiness Workforce
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 20 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, e40
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
2025 Reviewers
-
- Journal:
- Management and Organization Review / Volume 21 / Issue 6 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1265-1266
-
- Article
- Export citation