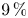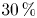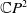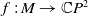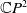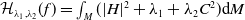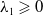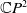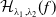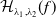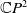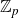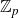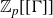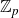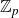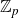Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419237 results in Open Access
The effect of albumın and total proteın values as nutrıtıonal markers after Fontan surgery on prognosıs
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, pp. 734-739
-
- Article
- Export citation
The odd octopus: identification and burrowing behaviour of a deep-water octopus, Muusoctopus leioderma, found in a shallow-water bay
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 103 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, e79
-
- Article
- Export citation
Compressibility effects in supersonic and hypersonic turbulent boundary layers subject to wall disturbances
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, A32
-
- Article
- Export citation
Axes to Axes: the Chronology, Distribution and Composition of Recent Bronze Age Hoards from Britain and Northern Ireland
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Prehistoric Society / Volume 89 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, pp. 179-205
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Lift generation mechanism of the leading-edge vortex for an unsteady plate
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, A30
-
- Article
- Export citation
Precarious work and challenger parties: how precarity influenced vote choice in the 2018 Italian election
-
- Journal:
- Italian Political Science Review / Rivista Italiana di Scienza Politica / Volume 54 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, pp. 17-35
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Social development and biodiversity conservation synergies for the West African giraffe in a human–wildlife landscape
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Environmental Conservation / Volume 50 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, pp. 259-266
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Helfrich functional for compact surfaces in
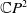 $\mathbb{C}P^{2}$
$\mathbb{C}P^{2}$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 66 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, pp. 36-50
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Enhancing Triage and Management in Earthquake-Related Injuries: The SAFE-QUAKE Scoring System for Predicting Dialysis Requirements
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 38 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, pp. 716-724
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Modelling and scaling laws of the ion emission regime in Taylor cones
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, A34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Better than Best: Epistemic Landscapes and Diversity of Practice in Science
-
- Journal:
- Philosophy of Science / Volume 91 / Issue 5 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, pp. 1189-1198
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Short-term cortisol adaption to discrimination and Mexican-origin adolescents’ mental and sleep health
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 36 / Issue 4 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, pp. 1863-1875
-
- Article
- Export citation
How Forced Switches Reveal Switching Costs: Evidence from the Loan Market
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis / Volume 59 / Issue 8 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, pp. 3994-4034
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Apparent singularities of the finite-depth Zakharov equation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, A35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Structure of fine Selmer groups over
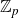 $\mathbb{Z}_{p}$-extensions
$\mathbb{Z}_{p}$-extensions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society / Volume 176 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, pp. 287-308
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Where memory resides: Is there a rivalry between molecular and synaptic models of memory?
-
- Journal:
- Philosophy of Science / Volume 91 / Issue 5 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, pp. 1382-1392
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Large eddy simulations of bubbly flows and breaking waves with smoothed particle hydrodynamics
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2023, A24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Molecular evidence for the first records and range extension of the great seahorse (Hippocampus kelloggi, Jordan & Snyder, 1901) in Quelimane, central coast of Mozambique
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 103 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2023, e77
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Microbubble formation by flow focusing: role of gas and liquid properties, and channel geometry
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2023, A27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Detailed numerical investigation of the drop aerobreakup in the bag breakup regime
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2023, A28
-
- Article
- Export citation