Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1382306 results in Open Access
Epizoic diatom diversity and abundance of on the spider crab Hyastenus hilgendorfi from Lake Timsah, Suez Canal, Egypt
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 106 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2026, e16
-
- Article
- Export citation
ON THE GROWTH OF TORSION IN THE COHOMOLOGY OF SOME ARITHMETIC GROUPS OF
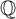 $\mathbb {Q}$-RANK ONE
$\mathbb {Q}$-RANK ONE
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2026, pp. 1-52
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
To insure or to smooth? Paternalistic rationales for mandatory retirement funding
-
- Journal:
- Economics & Philosophy , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2026, pp. 1-21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Renal replacement therapy after paediatric heart transplant: who gets it and associated outcomes
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2026, pp. 1-4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
CJN volume 53 issue 1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 53 / Issue 1 / January 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2026, pp. f1-f5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Truncated Jacobi triple product series II: Li, Lin, and Wang’s nonnegativity conjecture – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2026, p. 1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
“The Net That Catches the Most Fish”: Fishing, Innovation, and Law in the Gold Coast Colony (Ghana), c. 1898–1923
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of African History / Volume 67 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2026, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Everyday transactions in transit: Contextualizing coins in the ports of Berenike and Myos Hormos
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Roman Archaeology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2026, pp. 1-35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A monumental garden complex in Tabriz, Iran
-
- Journal:
- Antiquity , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2026, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Network co-activation relates to executive function following pediatric traumatic brain injury
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2026, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Highly Purified Cannabidiol Treatment Outcomes in Pediatric Patients with Highly Refractory Epilepsy at Tertiary Center
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2026, pp. 1-26
-
- Article
- Export citation
English signage around U.S. military bases in Japan: Insights from linguistic landscape research
-
- Journal:
- English Today , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2026, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Microstreaming induced by a micro-cantilever vibrating elliptically in a viscous fluid
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1028 / 10 February 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2026, A11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Politique Inc. La démocratie et les médias à l’ère du marketing Émilie Foster , Québec : Presses de l’Université Laval, 2025, 182 p.
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Political Science/Revue canadienne de science politique , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2026, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
FLM volume 1027 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1027 / 25 January 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2026, p. f1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Comeback of Natural Philosophy. Essay Review of Penelope Maddy, A Plea for Natural Philosophy and Other Essays
-
- Journal:
- Philosophy of Science / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2026, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
EARLY CHRISTIAN TEXTS TRANSLATED - Vittorio Berti / Emanuela Colombi / Carla Noce (edd.), Translation Dynamics in Early Christian Literature. (Corpus Christianorum Lingua Patrum 16.) Pp. 500. Turnhout: Brepols, 2024. Cased, €290. ISBN: 978-2-503-61080-1.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2026, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
Age, growth and mortality of the European Barracuda Sphyraena sphyraena (Linnaeus, 1758) from Eastern Algeria
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 106 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2026, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Using facial morphology traits related to attention problems in children to identify prenatal exposure history – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 17 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2026, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Radiocarbon analysis of mixed-sources plastic: Implementing approach at LAPA14C-UFBA
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2026, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation