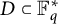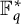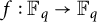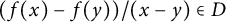Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418155 results in Open Access
ENT An Introduction and Practical Guide 3rd Edition - James Tysome, Rahul Kanegaonkar (eds) Published May 22, 2023 by CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group ISBN 9781032259611 (paperback) ISBN 9781032261973 (hardback) 186 Pages Price Paperback £39.99 Hardback £99.99 eBook £35.99
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 139 / Issue 6 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, p. 526
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Between the Client and the Institutional System: Street-level Bureaucrats’ Discretion, Positioning, and Trust in Institutional Encounters with Forced Migrants in Finland and Sweden
-
- Journal:
- Social Policy and Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comment on ‘Sarcopenic obesity in patients with head and neck cancer is predictive of critical weight loss during radiotherapy’
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 133 / Issue 2 / 28 January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, pp. 211-212
- Print publication:
- 28 January 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Utilising mitochondrial barcode sequencing to evaluate phylogeographical structure and guide the release of illegally traded Amazon parrots
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 34 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, e43
-
- Article
- Export citation
Reply to comment on ‘Sarcopenic obesity in patients with head and neck cancer is predictive of critical weight loss during radiotherapy’ (BJN-2-2024-1107)
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 133 / Issue 1 / 14 January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, pp. 82-83
- Print publication:
- 14 January 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Evolution of Umbrella Clauses and the Interpretation of Chinese Concession Loan Agreements in Nigeria
-
- Journal:
- Journal of African Law / Volume 69 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, pp. 93-108
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
A SUFFICIENT CONDITION FOR PANCYCLIC GRAPHS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 112 / Issue 2 / October 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, pp. 220-226
- Print publication:
- October 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Moderate deviations of many-server queues via idempotent processes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, pp. 708-742
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Famine at birth: long-term health effects of the 1974–75 Bangladesh famine
-
- Journal:
- Environment and Development Economics / Volume 30 / Issue 3 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, pp. 220-240
-
- Article
- Export citation
A compact wideband high-gain circularly polarized array antenna based on SIGW-SRP
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 17 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, pp. 92-103
-
- Article
- Export citation
Alex Egodotaye Asakitikpi and Aretha Oluwakemi Asakitikpi. Modern Nigeria: Understanding Modern Nations. New York: Bloomsbury, 2024. xix + 380 pp. Appendix. Bibliography. Index. $90. Hardcover. ISBN: 9781440865565.
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 68 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, pp. 405-406
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Bilinear Kloosterman sums in function fields and the distribution of irreducible polynomials
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, pp. 1-26
-
- Article
- Export citation
THG volume 27 issue 4-5 Cover
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 27 / Issue 4-5 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, p. f1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Local spiky contacts during impact of an emulsion drop on a solid surface
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1001 / 25 December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, A60
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mixed-methods multicenter assessment of healthcare workers’ knowledge, perceptions, and practices related to blood culture utilization in hospitalized adults
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 46 / Issue 2 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, pp. 156-164
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
A model of safe asset shortage and property taxes in China
-
- Journal:
- Macroeconomic Dynamics / Volume 29 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, e64
-
- Article
- Export citation
Asymptotics for the conditional higher moment coherent risk measure with weak contagion
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA / Volume 55 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, pp. 121-143
- Print publication:
- January 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
A strengthening of McConnel’s theorem on permutations over finite fields
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 68 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, pp. 213-218
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Retest reliability and reliable change of community-dwelling Black/African American older adults with and without mild cognitive impairment using NIH Toolbox-Cognition Battery and Cogstate Brief Battery for laptop
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 31 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, pp. 42-52
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Calendar of Short Courses and Workshops: (Occurring after 1 January 2025)
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 39 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2024, p. 293
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation