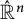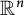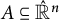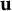Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1418667 results in Open Access
Assessment of the Relationship Between Amino Acid Status and Parkinson’s Disease: A Comprehensive Review and Meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 52 / Issue 4 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2024, pp. 606-622
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Birgit Sandkaulen, The Philosophy of Friedrich Heinrich Jacobi: On the Contradiction between System and Freedom (Bloomsbury Studies in Modern German Philosophy), translated by Matt Erlin. London: Bloomsbury Academic, 2023. ISBN 978-1-350-23571-7. Pp. 280. Hardback 90.00 Pound, Paperback 28.99 Pound, Ebook 26.09 Pound.
-
- Journal:
- Hegel Bulletin , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2024, pp. 1-5
-
- Article
- Export citation
Vitamin D and other micronutrient deficiency prevention: the role of data in informing national, regional and global policy
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Hascherkeller rectangular farmstead and its implications for Hallstatt social complexity
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
In memory of James C. Scott
-
- Journal:
- TRaNS: Trans-Regional and -National Studies of Southeast Asia / Volume 12 / Issue 2 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2024, p. 221
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Changing World of Spirit in Hegel’s Philosophy of Right
-
- Journal:
- Hegel Bulletin , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Average distance in a general class of scale-free networks
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2024, pp. 371-406
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Compact multiband cuff button antenna for WBAN application
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 16 / Issue 10 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2024, pp. 1739-1748
-
- Article
- Export citation
Improving Computer Vision Interpretability: Transparent Two-Level Classification for Complex Scenes
-
- Journal:
- Political Analysis / Volume 33 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2024, pp. 107-121
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
How enriched diet of the second trophic level (Tyrophagus putrescentiae) affects the performance of the third trophic level (Neoseiulus cucumeris): the role of pollens and legumes
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 6 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2024, pp. 869-875
-
- Article
- Export citation
Drawing the Jewish Propter Nos: Nineteenth-Century Missions and the Making of Race
-
- Journal:
- Comparative Studies in Society and History / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2024, pp. 116-140
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Challenges and Implications of Providing Continuous Care for the Elderly in Disaster Situations: A Case Study from the Noto Peninsula Earthquake
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 18 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2024, e307
-
- Article
- Export citation
The role of n-3 fatty acids in acute pancreatitis
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 133 / Issue 2 / 28 January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2024, pp. 221-230
- Print publication:
- 28 January 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Existential Happiness
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Philosophy / Volume 53 / Issue 6 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2024, pp. 463-471
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The dynamics of concentration fluctuations within passive scalar plumes in a turbulent neutral boundary layer
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1001 / 25 December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2024, A18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On polar convexity in finite-dimensional Euclidean spaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2024, pp. 1-37
-
- Article
- Export citation
Biorefined perennial ryegrass press cake as an alternative feed for dairy cows in late lactation and during the dry period: a demonstration
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 162 / Issue 5 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2024, pp. 528-537
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cosmos-Politanism: Transhumanist Visions of Global Order from the First World War to the Digital Age
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics / Volume 23 / Issue 3 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2024, pp. 1071-1088
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Sampling from the random cluster model on random regular graphs at all temperatures via Glauber dynamics
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2024, pp. 359-391
-
- Article
- Export citation
An Oligocene chimaeroid egg capsule from western Washington State, USA, and priority of Vaillantoonia Meunier, 1891
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 98 / Issue 5 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2024, pp. 910-913
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation