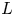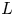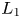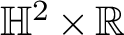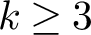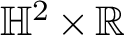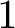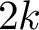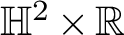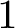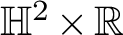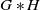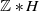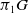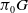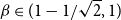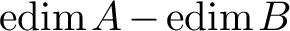Refine search
Actions for selected content:
25841 results in Abstract analysis
Graded identities for algebras with elementary gradings over an infinite field
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 65 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2022, pp. 146-166
-
- Article
- Export citation
Equivariant stable sheaves and toric GIT
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2022, pp. 385-416
- Print publication:
- April 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
A sandwich in thin lie algebras
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 65 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2022, pp. 136-145
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Periodic solutions of p-Laplacian differential equations with jumping nonlinearity across half-eigenvalues
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2022, pp. 307-326
- Print publication:
- February 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation

Classical and Discrete Functional Analysis with Measure Theory
-
- Published online:
- 06 January 2022
- Print publication:
- 20 January 2022
GENUS
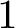 $1$ MINIMAL k-NOIDS AND SADDLE TOWERS IN
$1$ MINIMAL k-NOIDS AND SADDLE TOWERS IN 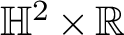 $\mathbb {H}^2\times \mathbb {R}$
$\mathbb {H}^2\times \mathbb {R}$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 22 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2022, pp. 2155-2175
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
GYSIN TRIANGLES IN THE CATEGORY OF MOTIFS WITH MODULUS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 22 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2022, pp. 2131-2154
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Weak amenability of free products of hyperbolic and amenable groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 64 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2022, pp. 698-701
-
- Article
- Export citation
Principal bundles on two-dimensional CW-complexes with disconnected structure group
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 64 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2022, pp. 675-690
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hausdorff dimension of the set of almost convergent sequences
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 64 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2022, pp. 691-697
-
- Article
- Export citation
Independent sets of a given size and structure in the hypercube
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 31 / Issue 4 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2022, pp. 702-720
-
- Article
- Export citation
JMJ volume 21 Issue 1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 21 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2022, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- January 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
JMJ volume 21 Issue 1 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 21 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2022, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- January 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Some generating functions and inequalities for the andrews–stanley partition functions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 65 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2021, pp. 120-135
-
- Article
- Export citation
Commutator length of powers in free products of groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 65 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2021, pp. 102-119
-
- Article
- Export citation
Macroscopic limit of a kinetic model describing the switch in T cell migration modes via binary interactions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 34 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 December 2021, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Periodic solutions for one-dimensional nonlinear nonlocal problem with drift including singular nonlinearities
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 December 2021, pp. 229-261
- Print publication:
- February 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
A FREENESS CRITERION WITHOUT PATCHING FOR MODULES OVER LOCAL RINGS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 22 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2021, pp. 2117-2129
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Series expansion of Leray–Trudinger inequality
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2021, pp. 262-274
- Print publication:
- February 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Index estimates for closed minimal submanifolds of the sphere
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 December 2021, pp. 802-816
- Print publication:
- June 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation