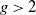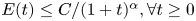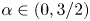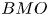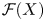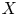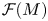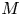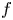Refine search
Actions for selected content:
25845 results in Abstract analysis
Abelian actions on compact nonorientable Riemann surfaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 64 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 December 2021, pp. 634-648
-
- Article
- Export citation
Decay of weak solutions to Vlasov equation coupled with a shear thickening fluid
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 December 2021, pp. 167-176
- Print publication:
- February 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Variational characterizations of weighted Hardy spaces and weighted $BMO$
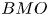 spaces
spaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2021, pp. 1613-1632
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
RETRACTED - Compact reduction in Lipschitz-free spaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 151 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 December 2021, pp. 1683-1699
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
A few remarks on Pimsner–Popa bases and regular subfactors of depth 2
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 64 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2021, pp. 586-602
-
- Article
- Export citation
PRM volume 151 issue 6 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 151 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 December 2021, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
PRM volume 151 issue 6 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 151 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 December 2021, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Inverse scattering transforms for non-local reverse-space matrix non-linear Schrödinger equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 33 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2021, pp. 1062-1082
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Partial regularity for minimizers of discontinuous quasiconvex integrals with general growth
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2021, pp. 1191-1232
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
TWISTED DOUBLING INTEGRALS FOR BRYLINSKI–DELIGNE EXTENSIONS OF CLASSICAL GROUPS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 22 / Issue 4 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2021, pp. 1931-1985
- Print publication:
- July 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Non-bifurcation of critical periods from semi-hyperbolic polycycles of quadratic centres
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2021, pp. 104-114
- Print publication:
- February 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Compact reduction in Lipschitz-free spaces - RETRACTION
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 151 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2022, p. 2082
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Frucht property in the quantum group setting
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 64 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2021, pp. 603-633
-
- Article
- Export citation
A blurred view of Van der Waerden type theorems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 31 / Issue 4 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 November 2021, pp. 684-701
-
- Article
- Export citation
On a backward problem for nonlinear time fractional wave equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2021, pp. 1589-1612
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Crystal flex bases and the RUM spectrum
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 64 / Issue 4 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2021, pp. 735-761
-
- Article
- Export citation
On non-separated zero sequences of solutions of a linear differential equation – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 64 / Issue 4 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2021, p. 1037
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
On free subalgebras of varieties
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 65 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2021, pp. 89-101
-
- Article
- Export citation
Brittle fracture in linearly elastic plates
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2021, pp. 68-103
- Print publication:
- February 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
A criterion for normality of analytic mappings
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 65 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2021, pp. 80-88
-
- Article
- Export citation