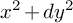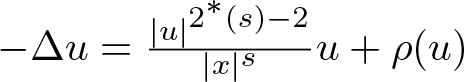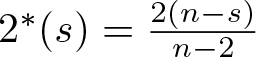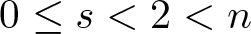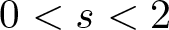Refine search
Actions for selected content:
25814 results in Abstract analysis
ON THE DEGREE OF IRRATIONALITY OF LOW GENUS
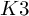 $K3$ SURFACES
$K3$ SURFACES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 3 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2025, pp. 627-662
- Print publication:
- May 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
STATED SKEIN MODULES OF 3-MANIFOLDS AND TQFT
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 3 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2025, pp. 663-703
- Print publication:
- May 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ON K-STABILITY OF CALABI-YAU FIBRATIONS
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 3 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2025, pp. 961-1019
- Print publication:
- May 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
3D Navier–Stokes–Voigt equations with damping and double delays on unbounded domains: Well-posedness, pullback attractors, and limit measures
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2025, pp. 1-39
-
- Article
- Export citation
COVERING INTEGERS BY
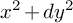 $x^2 + dy^2$
$x^2 + dy^2$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 3 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2025, pp. 847-889
- Print publication:
- May 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
PROJECTIVELY FLAT FOLIATIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 3 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2025, pp. 763-812
- Print publication:
- May 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
NOMBRE DE PETITS POINTS SUR UNE VARIÉTÉ ABÉLIENNE
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 3 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2025, pp. 705-761
- Print publication:
- May 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
SIMPLE TYPE THEORY FOR METAPLECTIC COVERS OF
 $\operatorname {GL}(r)$ OVER A NON-ARCHIMEDEAN LOCAL FIELD
$\operatorname {GL}(r)$ OVER A NON-ARCHIMEDEAN LOCAL FIELD
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 4 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2025, pp. 1263-1335
- Print publication:
- July 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The operad of Latin hypercubes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 67 / Issue 3 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 March 2025, pp. 475-486
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
MUKAI’S PROGRAM FOR NONPRIMITIVE CURVES ON K3 SURFACES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 3 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 March 2025, pp. 1053-1091
- Print publication:
- May 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
GAUSSIAN HOLOMORPHIC SECTIONS ON NONCOMPACT COMPLEX MANIFOLDS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 4 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 March 2025, pp. 1197-1262
- Print publication:
- July 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impact of prey-taxis on a harvested intraguild predation predator–prey model
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 36 / Issue 6 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 March 2025, pp. 1183-1220
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Pride–Guba–Sapir exact sequence for the relation bimodule of an associative algebra
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 67 / Issue 3 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 March 2025, pp. 467-474
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
From integro-differential models to data-oriented approaches for emergent phenomena
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 36 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 March 2025, p. 187
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A critical non-homogeneous heat equation with weighted source
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 36 / Issue 6 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2025, pp. 1148-1159
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
GAGA FOR HENSELIAN SCHEMES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 4 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 March 2025, pp. 1547-1589
- Print publication:
- July 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Unique compact representation of magnetic fields using truncated solid harmonic expansions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 36 / Issue 5 / October 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 March 2025, pp. 1012-1039
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Non-additive derived functors via chain resolutions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 67 / Issue 3 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2025, pp. 423-466
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Theory of heat equations for sigma functions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 67 / Issue 3 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2025, pp. 365-422
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On a perturbed critical semilinear equation with singularity
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2025, pp. 1-35
-
- Article
- Export citation
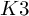



 of minimal degree and their variational structure. In particular, we prove that the degree of irrationality of all such surfaces is at most
of minimal degree and their variational structure. In particular, we prove that the degree of irrationality of all such surfaces is at most 

 of degree
of degree