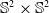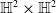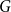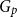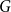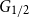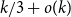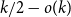Refine search
Actions for selected content:
25814 results in Abstract analysis
The Formanek-Procesi group with base a right-angled Artin group: Lie algebra and residual nilpotence
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 May 2025, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
- Export citation
CONTRACTING ENDOMORPHISMS OF VALUED FIELDS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 5 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 May 2025, pp. 2047-2106
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
FONCTIONS ADDITIVES EN BASE DE CANTOR LE LONG DES NOMBRES PREMIERS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 5 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 May 2025, pp. 1807-1865
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
On hypersurfaces of
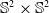 $\mathbb{S}^2\times \mathbb{S}^2$ and
$\mathbb{S}^2\times \mathbb{S}^2$ and 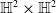 $\mathbb{H}^2\times \mathbb{H}^2$ with recurrent Ricci tensor
$\mathbb{H}^2\times \mathbb{H}^2$ with recurrent Ricci tensor
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 April 2025, pp. 1-21
-
- Article
- Export citation
Strongly reversible classes in SL(n, ℂ)
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 68 / Issue 4 / November 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 April 2025, pp. 1137-1168
-
- Article
- Export citation
Colouring random subgraphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 April 2025, pp. 585-595
-
- Article
- Export citation
Non-existence theorems for quasilinear elliptic equations with weights
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 April 2025, pp. 1-33
-
- Article
- Export citation
On Fock covariance for product systems and the reduced Hao–Ng isomorphism problem by discrete actions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 April 2025, pp. 1-53
-
- Article
- Export citation
Integral constraints in multiple scales problems with a slowly varying microstructure
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2025, pp. 1-21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
MOCK PLECTIC POINTS
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 5 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2025, pp. 2107-2131
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the long-time asymptotics of the modified Camassa–Holm equation with step-like initial data
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 April 2025, pp. 1-44
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Global dynamics for the generalised chemotaxis-Navier–Stokes system in
 $\mathbb{R}^3$
$\mathbb{R}^3$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2025, pp. 1-38
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Diagrammatics for the smallest quantum coideal and Jones–Wenzl projectors
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2025, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
- Export citation
Homogenised models of nutrient transport in a fibrous bioreactor scaffold
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 April 2025, pp. 1-28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On an open problem of value sharing and differential equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 68 / Issue 4 / November 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2025, pp. 1110-1136
-
- Article
- Export citation
Optimal transport on gas networks
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2025, pp. 1-33
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
GENERAL HYPERPLANE SECTIONS OF LOG CANONICAL THREEFOLDS IN POSITIVE CHARACTERISTIC
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 5 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2025, pp. 1867-1894
- Print publication:
- September 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Instability of axisymmetric flow in thermocapillary liquid bridges: Kinetic and thermal energy budgets for two-phase flow with temperature-dependent material properties – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 36 / Issue 6 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2025, pp. 1221-1225
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Optimal control of a reaction-diffusion epidemic model with non-compliance
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2025, pp. 1-26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Regularity of quasigeodesics characterizes hyperbolicity
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2025, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation