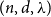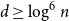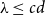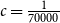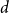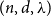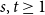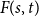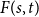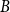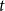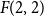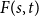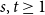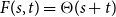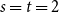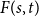Refine search
Actions for selected content:
25814 results in Abstract analysis
Newton–Maclaurin type inequalities for linear combinations of elementary symmetric functions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2025, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
- Export citation
Derived functors and Hilbert polynomials over hypersurface rings
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 68 / Issue 3 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2025, pp. 898-908
-
- Article
- Export citation
Remark on the local well-posedness for NLS with the modulated dispersion
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2025, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Numerical solution of a PDE arising from prediction with expert advice
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2025, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Solutions with prescribed mass for L2-supercritical NLS equations under Neumann boundary conditions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2025, pp. 1-34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Spatio-temporal dynamics of a lattice prey–predator system with non-local diffusion in a periodic habitat
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 March 2025, pp. 1-43
-
- Article
- Export citation
A logarithmic uncertainty principle for functions with radial symmetry
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 68 / Issue 3 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 March 2025, pp. 811-824
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hardy and Rellich Inequalities with Bessel Pairs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 68 / Issue 3 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 March 2025, pp. 825-842
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Bounds on the Pythagoras number and indecomposables in biquadratic fields
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 68 / Issue 3 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 March 2025, pp. 843-868
-
- Article
- Export citation
GMJ volume 67 issue 2 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 67 / Issue 2 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 March 2025, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- May 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Every locally compact group is the outer automorphism group of a II1 factor
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 March 2025, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
GMJ volume 67 issue 2 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 67 / Issue 2 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 March 2025, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- May 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
How to beat a Bayesian adversary
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 March 2025, pp. 1-23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
TEICHMÜLLER CURVES IN HYPERELLIPTIC COMPONENTS OF MEROMORPHIC STRATA
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 4 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 March 2025, pp. 1521-1546
- Print publication:
- July 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Iterating additive polynomials over finite fields
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 68 / Issue 3 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2025, pp. 795-810
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hamiltonicity of sparse pseudorandom graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2025, pp. 596-620
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A note on digraph splitting
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2025, pp. 559-564
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Linearity of compact R-analytic groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 68 / Issue 3 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2025, pp. 787-794
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Tate duality and transfer for symmetric algebras over complete discrete valuation rings
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 68 / Issue 3 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2025, pp. 763-786
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
TWISTED BLANCHFIELD PAIRINGS AND TWISTED SIGNATURES II: RELATION TO CASSON-GORDON INVARIANTS
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 4 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 March 2025, pp. 1139-1195
- Print publication:
- July 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation