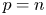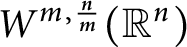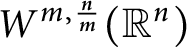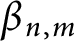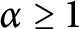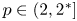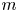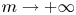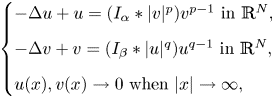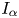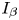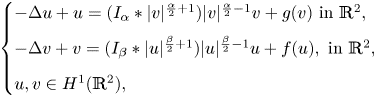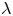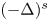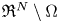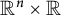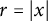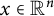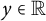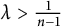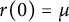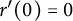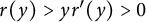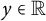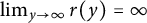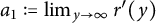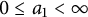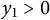Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
415 results in 35Jxx
Stationary solutions to the Keller–Segel equation on curved planes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2022, pp. 327-343
- Print publication:
- February 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Bifurcation of elastic curves with modulated stiffness
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 34 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 January 2022, pp. 28-54
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Necessary and sufficient conditions on global solvability for the p-k-Hessian inequalities
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 65 / Issue 4 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2022, pp. 1004-1019
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Periodic solutions for one-dimensional nonlinear nonlocal problem with drift including singular nonlinearities
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 December 2021, pp. 229-261
- Print publication:
- February 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Series expansion of Leray–Trudinger inequality
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2021, pp. 262-274
- Print publication:
- February 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Optimal Hardy-weights for the (p, A)-Laplacian with a potential term
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 December 2021, pp. 289-306
- Print publication:
- February 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A sharpened form of Adams-type inequalities on higher-order Sobolev spaces
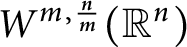 $W^{m,\frac {n}{m}}(\mathbb {R}^n)$: a simple approach
$W^{m,\frac {n}{m}}(\mathbb {R}^n)$: a simple approach
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 65 / Issue 4 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2021, pp. 895-905
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Partial regularity for minimizers of discontinuous quasiconvex integrals with general growth
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2021, pp. 1191-1232
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Anisotropic Gauss curvature flows and their associated Dual Orlicz-Minkowski problems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 November 2021, pp. 148-162
- Print publication:
- February 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Existence results for a nonlinear nonautonomous transmission problem via domain perturbation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 October 2021, pp. 1451-1476
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Concentrating standing waves for Davey–Stewartson systems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 October 2021, pp. 1411-1450
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Asymptotic behaviour of positive solutions of semilinear elliptic problems with increasing powers
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 September 2021, pp. 1233-1250
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Existence and nonexistence results for a class of Hamiltonian Choquard-type elliptic systems with lower critical growth on ℝ2
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 September 2021, pp. 1383-1410
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
PDE comparison principles for Robin problems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 75 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2021, pp. 108-139
- Print publication:
- February 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Bifurcation structure of coexistence states for a prey–predator model with large population flux by attractive transition
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 4 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 August 2021, pp. 965-988
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Positive solutions for a degenerate Kirchhoff problem
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 64 / Issue 3 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2021, pp. 675-688
-
- Article
- Export citation
On sectoriality of degenerate elliptic operators
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 64 / Issue 3 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 August 2021, pp. 689-710
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the fractional Lazer-McKenna conjecture with critical growth
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 4 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 August 2021, pp. 879-911
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Existence of hypercylinder expanders of the inverse mean curvature flow
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 65 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2021, pp. 543-551
- Print publication:
- September 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nehari–Pohožaev-type ground state solutions of Kirchhoff-type equation with singular potential and critical exponent
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 65 / Issue 2 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 June 2021, pp. 473-495
- Print publication:
- June 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation