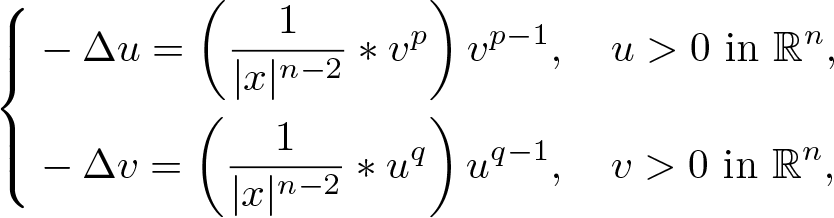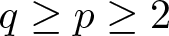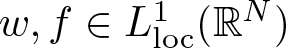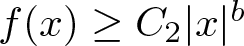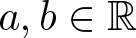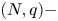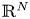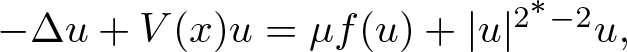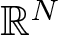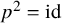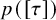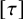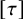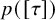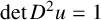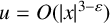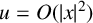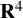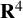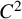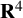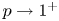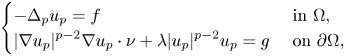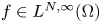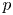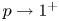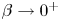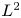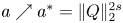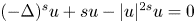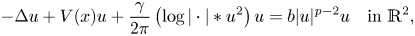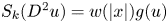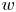Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
415 results in 35Jxx
On Liouville theorems of a Hartree–Poisson system
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 4 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 October 2023, pp. 1154-1178
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stable solutions to double phase problems involving a nonlocal term
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 4 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, pp. 1119-1141
-
- Article
- Export citation
A NOTE ON NORMALISED GROUND STATES FOR THE TWO-DIMENSIONAL CUBIC-QUINTIC NONLINEAR SCHRÖDINGER EQUATION
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 109 / Issue 3 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2023, pp. 552-561
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
A weighted Trudinger–Moser inequalities and applications to some weighted $(N,q)-$
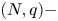 Laplacian equation in $\mathbb {R}^N$
Laplacian equation in $\mathbb {R}^N$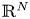 with new exponential growth conditions
with new exponential growth conditions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2023, pp. 124-175
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Normalized positive solutions for Schrödinger equations with potentials in unbounded domains
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 154 / Issue 5 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 1518-1551
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Combined effects in mixed local–nonlocal stationary problems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 10-56
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
A non-periodic indefinite variational problem in ℝN with critical exponent
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 2 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 June 2023, pp. 579-612
-
- Article
- Export citation
Groundstates of the planar Schrödinger–Poisson system with potential well and lack of symmetry
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 154 / Issue 4 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2023, pp. 993-1023
- Print publication:
- August 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Local regularity for nonlinear elliptic and parabolic equations with anisotropic weights
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 2 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 April 2023, pp. 391-436
-
- Article
- Export citation
Biharmonic almost complex structures
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 March 2023, e25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
THE GROWTH OF SOLUTIONS OF MONGE–AMPÈRE EQUATIONS IN HALF SPACES AND ITS APPLICATION
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 109 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 March 2023, pp. 125-137
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Radial solvability for Pucci-Lane-Emden systems in annuli
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 154 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 March 2023, pp. 494-507
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
COMPACTNESS AND STRUCTURE OF ZERO-STATES FOR UNORIENTED AVILES–GIGA FUNCTIONALS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 23 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 March 2023, pp. 941-982
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dimension reduction analysis of a three-dimensional thin elastic plate reinforced with fractal ribbons
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 March 2023, pp. 838-869
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stable anisotropic minimal hypersurfaces in
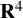 $\mathbf {R}^{4}$
$\mathbf {R}^{4}$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Pi / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2023, e3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Behaviour of solutions to p-Laplacian with Robin boundary conditions as p goes to 1
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 154 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2023, pp. 105-130
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
On a quasilinear elliptic problem involving the 1-Laplacian operator and a discontinuous nonlinearity
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 154 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 December 2022, pp. 33-59
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Concentration behaviour of normalized ground states of the mass critical fractional Schrödinger equations with ring-shaped potentials
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2022, pp. 1993-2024
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
On a planar Schrödinger–Poisson system involving a non-symmetric potential
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 65 / Issue 4 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 December 2022, pp. 1133-1146
-
- Article
- Export citation
Some results for semi-stable radial solutions of k-Hessian equations with weight on ℝn
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2022, pp. 1751-1776
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation