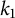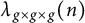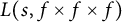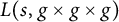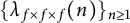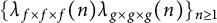Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419634 results in Open Access
Transcatheter closure of a large aortopulmonary window using a Lifetech™ Konar-MF occluder device
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 9 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2024, pp. 2022-2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Anticoagulation with warfarin for paediatric cardiac indications: a retrospective study
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 35 / Issue 2 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2024, pp. 407-412
-
- Article
- Export citation
The prefrontal cortex, but not the medial temporal lobe, is associated with episodic memory in middle-aged persons with HIV
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 30 / Issue 10 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2024, pp. 966-976
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Squamous cell carcinoma of the posterior pharyngeal wall: A comparative analysis of oropharyngeal origin versus hypopharyngeal origin
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 139 / Issue 7 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2024, pp. 582-586
- Print publication:
- July 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
High-order-mode cavity fed 45° linear polarized antenna for 5G applications
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 16 / Issue 9 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2024, pp. 1570-1578
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mark Stoyle. A Murderous Midsummer: The Western Rising of 1549 New Haven: Yale University Press, 2022. Pp. 384. $60.00 (cloth).
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 63 / Issue 4 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2024, pp. 922-924
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ediacaran paleobiology and biostratigraphy of the Nama Group, Namibia, with emphasis on the erniettomorphs, tubular and trace fossils, and a new sponge, Arimasia germsi n. gen. n. sp.
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 98 / Issue S94 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2024, pp. 1-59
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Advancing nutritional disorder classification: unleashing the impact of ICD-11 on clinical practice and public health
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 133 / Issue 1 / 14 January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2024, pp. 11-12
- Print publication:
- 14 January 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Substrate integrated waveguide differential antenna for full duplex applications
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 16 / Issue 9 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2024, pp. 1540-1546
-
- Article
- Export citation
An extended review of Maura Dykstra, Uncertainty in the Empire of Routine: The Administrative Revolution of the Eighteenth-Century Qing State. (Harvard East Asian Monographs Series.) Cambridge: Harvard University Asia Center, 2022. xxxv, 262 pp. ISBN 978 0 674 27095 4.
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies / Volume 88 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2024, pp. 149-161
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
QUASI-ERGODICITY OF COMPACT STRONG FELLER SEMIGROUPS ON
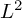 $L^2$
$L^2$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 2 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2024, pp. 541-584
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Technopolitics, development and the residues of the South African state
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal for the History of Science / Volume 57 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2024, pp. 645-649
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Citizenship in the shadow of law: identifying the origins, effects, and operation of legal ambiguity in Jordan
-
- Journal:
- Law & Society Review / Volume 58 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2024, pp. 573-606
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mitigating Missingness in Analysing Chinese Policy and Implications for the Fragility of Our Knowledge Base
-
- Journal:
- The China Quarterly / Volume 261 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2024, pp. 234-248
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of the shape of microswimmers and slip boundary conditions on the dynamic characteristics of near-wall microswimmers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 999 / 25 November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2024, A42
-
- Article
- Export citation
Internal tides and the inviscid dynamics of an oscillating ellipsoid in a stratified fluid
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 999 / 25 November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2024, A59
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comparison of single-step methods for genomic prediction of age at first calving in dairy buffaloes
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 162 / Issue 4 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2024, pp. 377-383
-
- Article
- Export citation
Guided-jet waves
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 999 / 25 November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2024, A47
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the sign changes of Dirichlet coefficients of triple product L-functions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 67 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2024, pp. 1092-1106
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation

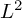








 . We discuss several applications and illustrate our results with examples. This includes a complete description of quasi-ergodicity for a large class of semigroups corresponding to non-local Schrödinger operators with confining potentials.
. We discuss several applications and illustrate our results with examples. This includes a complete description of quasi-ergodicity for a large class of semigroups corresponding to non-local Schrödinger operators with confining potentials.