Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1382371 results in Open Access
Dispersive shock waves in gravity-capillary free-surface flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1028 / 10 February 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 February 2026, A33
-
- Article
- Export citation
Curriculum and assessment in music education
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Music Education / Volume 42 / Issue 3 / November 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 February 2026, pp. 267-270
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Coprolite-filled borings: insight into the life history of detritivorous Pennsylvanian terrestrial arthropods
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 February 2026, pp. 1-15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cohomology of restricted twisted Heisenberg Lie algebras – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 February 2026, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
BME volume 42 issue 3 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Music Education / Volume 42 / Issue 3 / November 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 February 2026, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Senate Sandbox: Teaching Legislative Politics through Open-ended, Multi-week Simulations
-
- Journal:
- PS: Political Science & Politics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 February 2026, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Semiframes: the algebra of semitopologies and actionable coalitions
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Structures in Computer Science / Volume 36 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 February 2026, e3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
IMA Commission on New Minerals, Nomenclature and Classification (CNMNC) – Newsletter 89
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 February 2026, pp. 1-5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
THE CLASS OF THE PRYM-BRILL-NOETHER DIVISOR
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 February 2026, pp. 1-30
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Vushko, Iryna. Lost Fatherland: Europeans between Empire and Nation-States, 1867–1939. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2024. Pp. 352. – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Austrian History Yearbook , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2026, p. 1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
PROOF OF A CONJECTURE OF GARVAN AND JENNINGS-SHAFFER ON NONNEGATIVITY OF
 $M_{C1}(m,n)$ AND
$M_{C1}(m,n)$ AND 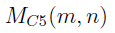 $M_{C5}(m,n)$
$M_{C5}(m,n)$
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2026, pp. 1-23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Prioritising cultural food security and food sovereignty over conventional food security: A multi-dimensional analytical argument
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2026, pp. 1-31
-
- Article
- Export citation
Survey of hemodialysis patients’ knowledge of their infection risk and acceptability of an intranasal decolonization intervention
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2026, pp. 1-5
-
- Article
- Export citation
A new age for the initiation of an overflowing Lake Gunnison and the regressive phase of Lake Bonneville
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2026, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Bridging Sonic Borders: Popular Music in Contemporary Dominican/Dominicanyork Literature. By Sharina Maíllo-Pozo. Austin: University of Texas Press, 2025. 229 pp. ISBN 978-1-4773-3155-2.
-
- Journal:
- Popular Music , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2026, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Judging at a Distance: The Effects of Remote Hearings during the COVID-19 Pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Law & Social Inquiry , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2026, pp. 1-21
-
- Article
- Export citation
NASSER RABBAT and DEEN SHARP, eds. Reconstruction as Violence in Assad’s Syria (Cairo: American University of Cairo, 2025). 262 pages. $79.95 hardcover and e-book. ISBN 9781649034137
-
- Journal:
- Review of Middle East Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2026, pp. 1-4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The visual construction of Vasily Eroshenko’s image in China: Media, memory, and “loneliness” through Chu Baoheng’s photography
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Asian Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2026, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The ‘swastika epidemic’ of 1960 and the first major public debate about antisemitism in republican Italy – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Modern Italy , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2026, p. 1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On Class Groups of Abelian Extensions
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2026, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation