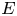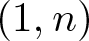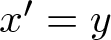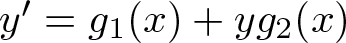Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419394 results in Open Access
Attenuating surface gravity waves with an array of submerged resonators: an experimental study
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 973 / 25 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, A16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Bicategorical type theory: semantics and syntax
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Structures in Computer Science / Volume 33 / Issue 10 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, pp. 868-912
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Caroline E. Foster, Global Regulatory Standards in Environmental and Health Disputes: Regulatory Coherence, Due Regard, and Due Diligence Oxford University Press, 2021, 371 pages.
-
- Journal:
- World Trade Review / Volume 23 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, pp. 112-115
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Inertial wave attractors in librating cuboids
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 973 / 25 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, A20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chuko Esiri and Arie Esiri, directors. Eyimofe (This Is My Desire). 2020. 114 minutes. Nigeria. English, Nigerian Pidgin, Yoruba. GDN Studios, Kimiera, Ominira Studios. No price reported. – ADDENDUM
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 66 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, p. 1119
-
- Article
- Export citation
Testing guidelines for distinctness, uniformity and stability in Oxalis
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 21 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, pp. 304-311
-
- Article
- Export citation
Special issue on speech representation in Late Modern English text types: introduction
-
- Journal:
- English Language & Linguistics / Volume 27 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, pp. 437-445
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Exploring a Mallorca cave flooding during the Little Ice Age using nondestructive techniques on a stalagmite: micro-CT and XRF core scanning
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 118 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, pp. 75-87
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
World Heritage Sites and the question of scale in governance and politics: A study of Stonehenge
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Cultural Property / Volume 30 / Issue 2 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, pp. 155-176
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Talking to peasants: language, place and class in British fiction 1800–1836
-
- Journal:
- English Language & Linguistics / Volume 27 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, pp. 543-560
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A weakened Markus–Yamabe condition for planar polynomial differential systems of degree
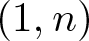 $(1,n)$
$(1,n)$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 4 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, pp. 1110-1118
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Home-inhaled nitric oxide in a child with pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with post-operative pulmonary venous obstruction
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 12 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, pp. 2673-2675
-
- Article
- Export citation
Analyse des bulletins de vote rejetés et de l'effet du rallye pour l'unité canadienne lors du référendum québécois de 1995
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Political Science/Revue canadienne de science politique / Volume 57 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, pp. 215-227
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Global Analysis of Transgender Rights: Introducing the Trans Rights Indicator Project (TRIP)
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, pp. 799-818
- Print publication:
- September 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Party and Party System Institutionalization: Which Comes First?
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics / Volume 22 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, pp. 194-212
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Blessing-Miles Tendi. The Army and Politics in Zimbabwe: Mujuru, the Liberation Fighter and Kingmaker. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2020. Contents. Index. Illustrations. Index. 339 pp. $130.00. Cloth. ISBN: 9781108472890.
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 66 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, pp. 1081-1083
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Indice du potentiel de participation sociale des Québécois âgés : cartographie des inégalités des zones métropolitaines, urbaines et rurales: IPPS : cartographie des inégalités
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement / Volume 43 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, pp. 84-98
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Flow over a circular cylinder with a flexible splitter plate
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 973 / 25 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, A19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
BIG IN REVERSE MATHEMATICS: MEASURE AND CATEGORY
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Symbolic Logic , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, pp. 1-46
-
- Article
- Export citation
Frictional boundary condition for lattice Boltzmann modelling of dense granular flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 973 / 25 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2023, A21
-
- Article
- Export citation