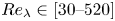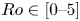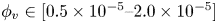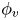Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419635 results in Open Access
Political Rage and the Value of Valuing
-
- Journal:
- Philosophy / Volume 98 / Issue 4 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 September 2023, pp. 451-475
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WTR volume 22 issue 3-4 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- World Trade Review / Volume 22 / Issue 3-4 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 September 2023, pp. b1-b7
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Understanding patterns of psychological distress associated with acculturation and caregiving among diverse Californian adults: Commentary on “Associations between caregiving status, acculturation, and psychological distress in a diverse sample” by Nguyen et al.
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 36 / Issue 8 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 625-627
-
- Article
- Export citation
ANCIENT ‘GLOBALISATION’ - (S.) Muthukumaran The Tropical Turn. Agricultural Innovation in the Ancient Middle East and the Mediterranean. Pp. xx + 294, ills, maps. Oakland, CA: University of California Press, 2023. Paper, £30, US$34.95 (Cased, £80, US$95). ISBN: 978-0-520-39084-3 (978-0-520-39083-6 hbk).
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 74 / Issue 1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 132-134
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Not Hidden but Not Visible: Government Funding of Independent Schools in Canada
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Political Science/Revue canadienne de science politique / Volume 56 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 698-714
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Spartans in the ancient Greek novels
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Hellenic Studies / Volume 143 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 121-146
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Elvis Sabin Ngaïbino, dir. Makongo. 2020. 72 min. Aka, Sango, French, with English Subtitles. Central African Republic, Italy, and Argentina. Makongo Films. No Price Reported.
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 864-865
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
GREEK AND ARMENIAN LITERATURE - (G.) Muradyan Ancient Greek Myths in Medieval Armenian Literature. (Armenian Texts and Studies 5.) Pp. xiv + 441. Leiden and Boston: Brill, 2022. Cased, €110. ISBN: 978-90-04-51979-4.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 74 / Issue 1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 314-315
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
An experimental study on the settling velocity of inertial particles in different homogeneous isotropic turbulent flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 970 / 10 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, A23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Convexity of the radial sum of a star body and a ball
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 67 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 289-303
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
A set of 2-recurrence whose perfect squares do not form a set of measurable recurrence
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 44 / Issue 6 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 1541-1580
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cambodia. Early Theravādin Cambodia: Perspectives from art and archaeology Edited by Ashley Thompson Singapore: National University of Singapore Press (with the Southeast Asian Art Academic Programme, SOAS University of London). Pp. xxix + 288. Maps, Images, Bibliography, Index.
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Southeast Asian Studies / Volume 54 / Issue 3 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 555-557
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Attempted Suicide: Its Social Significance and Effects by Erwin Stengel and Nancy Cook, with Irving Kreeger
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Advances / Volume 30 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 134-136
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
New Narratives and Old Myths: History Textbooks in Kazakhstan
-
- Journal:
- Nationalities Papers / Volume 52 / Issue 5 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 1193-1208
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nagasawa's Maximal God and the Ontological Argument
-
- Journal:
- Religious Studies / Volume 60 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 640-666
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Drug-related deaths among housed and homeless individuals in the UK and the USA: comparative retrospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 223 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 562-568
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
GODS AS SAVIOURS - (T.S.F.) Jim Saviour Gods and Soteria in Ancient Greece. Pp. xiv + 319, ills, maps. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2022. Cased, £75, US$100. ISBN: 978-0-19-289411-3.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 74 / Issue 1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 265-267
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Merely Means Paternalist? Prospect Theory and “Debiased” Welfare Analysis
-
- Journal:
- Philosophy of Science / Volume 91 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 204-224
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
CONVERSIONS IN THE ANCIENT WORLD - (A.) Despotis, (H.) Löhr (edd.) Religious and Philosophical Conversion in the Ancient Mediterranean Traditions. (Ancient Philosophy & Religion 5.) Pp. xii + 477, figs. Leiden and Boston: Brill, 2022. Cased, €149, US$180. ISBN: 978-90-04-50176-8.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 74 / Issue 1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 284-287
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
“You Needed to Accept the Situation”: Resilience of Nursing Home Residents in Times of COVID-19
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement / Volume 43 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 75-83
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation