Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1382372 results in Open Access
User guide for scanning electron microscopy applications to luminescence dating
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Objective Standards of Medical Judgment: A Myth of (Texas) Abortion Law
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Law, Medicine & Ethics ,
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Irish nurses in the NHS: an oral history. Edited by Louise Ryan , Gráinne McPolinand Neha Doshi . Pp 224. Dublin: Four Courts Press. 2025. £17.50/ €19.95 paperback.
-
- Journal:
- Irish Historical Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Peripheral Indicators of Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology in Women With Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Case–Control Study
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
FLM volume 1026 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1026 / 10 January 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, p. f1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
MDH volume 69 issue 4 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Medical History / Volume 69 / Issue 4 / October 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, p. f1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Post-operative practice patterns after the bidirectional Glenn surgery: a survey
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 36 / Issue 1 / January 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, pp. 164-170
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Leveraging a large language model to support expansion of surveillance activities to include cardiovascular implantable device infections in a large, integrated national healthcare system
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Irish first ladies and gentlemen, 1919–2011. By Bernadette Whelan . Pp xi, 426. Cork: Cork University Press. 2024. €49 hardback.
-
- Journal:
- Irish Historical Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Miklós Konrád. Jewishness and Beyond: Jewish Conversions in Hungary, 1825–1914. Translated by Jason Vincz and Miklós Konrád. Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press, 2024. Pp. 429.
-
- Journal:
- Austrian History Yearbook , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
Peter Adamson and Chike Jeffers, Africana Philosophy from Ancient Egypt to the Nineteenth Century (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2025). Pp. 528. £25.00 (Hbk). ISBN 9780198927174
-
- Journal:
- Religious Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, pp. 1-4
-
- Article
- Export citation
Triangles in the plane and arithmetic progressions in thick compact subsets of
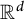 $\mathbb {R}^d$
$\mathbb {R}^d$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, pp. 1-41
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Liminal
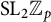 $\mathrm {SL}_2 \mathbb{Z}_{p}$-representations and odd-th cyclic covers of genus one two-bridge knots
$\mathrm {SL}_2 \mathbb{Z}_{p}$-representations and odd-th cyclic covers of genus one two-bridge knots
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Print and the Celtic languages: publishing and reading in Irish, Welsh, Gaelic and Breton, 1700–1900. By Niall Ó Ciosáin . Pp viii, 198. Abingdon and New York: Routledge, 2024. £145 hardback.
-
- Journal:
- Irish Historical Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Unusual right-to-left shunt in a patient with tricuspid atresia and stenosis of Fontan conduit
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 36 / Issue 1 / January 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, pp. 161-163
-
- Article
- Export citation
Imperial mobilities, errantry, and the displacement of the Chagos Islanders
-
- Journal:
- Review of International Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Constantin Ardeleanu. Steamboat Modernity Travel, Transport, and Social Transformation on the Lower Danube, 1830–1860. Translated by James Christian Brown. Budapest: Central European University Press, 2024. Pp. 264.
-
- Journal:
- Austrian History Yearbook , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Francine Friedman. Like Salt for Bread. The Jews of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Leiden: Brill, 2021. Pp. 946.
-
- Journal:
- Austrian History Yearbook , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
CJM volume 78 issue 1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 78 / Issue 1 / February 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, pp. f1-f3
- Print publication:
- February 2026
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Le soft power en Asie. Nouvelles formes de pouvoir et d’influence? Frédéric Lasserre, Éric Mottet et Barthélémy Courmont (dir.), Québec : Presses de l’Université du Québec, 2024, 334 p.
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Political Science/Revue canadienne de science politique , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation