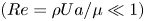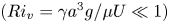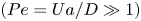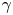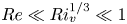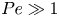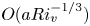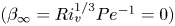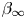Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1416025 results in Open Access
Yujin Nagasawa, The Problem of Evil for Atheists(Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2024). pp. xiii + 252. £ 76.00 (Hbk). ISBN 9780198901884.
-
- Journal:
- Religious Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 1-4
-
- Article
- Export citation
Leadership Reconfiguration in State-Acquired Privately Owned Enterprises: A Paradox between Institutional Control and Agency
-
- Journal:
- Management and Organization Review / Volume 20 / Issue 5 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 773-803
-
- Article
- Export citation
Improving the ability of psychiatric hospitals to respond to infectious disease outbreaks: lessons learned from the COVID-19 outbreak response in Ibaraki Prefecture, Japan
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 46 / Issue 2 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 218-219
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
More eggs are not more sires: long-term monogamy reduces fertility in a predatory ladybird
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 115 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 66-73
-
- Article
- Export citation
Similar host instar preferences by three sympatric parasitoids of Chielomenes sexmaculata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae): potential host niche overlapping
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 115 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 21-31
-
- Article
- Export citation
Exploring Differences in Stroke Treatment Between Urban and Rural Hospitals: A Thematic Analysis of Practices in Canada
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 52 / Issue 5 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 784-792
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Retrospective Evaluation of Anesthesia in Patients Undergoing Surgery after the February 6, 2023 Earthquake in Turkey
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 19 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, e10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Observer-rated environmental sensitivity and its characterization at behavioral, genetic, and physiological levels
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 1-15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Metamaterial based stepped microstrip line fed quad-band dual-sense circularly polarized slot antenna for wireless applications
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 17 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 113-131
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Case of Anomalous Origin of the Middle Cerebral Artery
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 52 / Issue 5 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 852-853
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prognostic value of the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition criteria including systemic inflammation in patients with advanced cancer
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 133 / Issue 2 / 28 January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 246-252
- Print publication:
- 28 January 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
La surveillance : un instrument d’évitement de l'intrusion militaire dans le champ politique camerounais
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Political Science/Revue canadienne de science politique / Volume 57 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 842-860
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Changes in juvenile hormone titres and differential expression of related genes at different stages of Coccinella septempunctata L. female adults supplied with an artificial diet and aphid diet
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 115 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 32-38
-
- Article
- Export citation
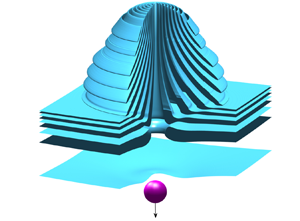
Mega-fortresses in the South Caucasus: new data from southern Georgia
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Functions with small BMO norm
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 1-15
-
- Article
- Export citation
Equivalences of stable categories of Gorenstein local rings
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 68 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 338-348
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
The flow field due to a sphere moving in a viscous, density-stratified fluid
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1002 / 10 January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, A44
-
- Article
- Export citation
Beurling type invariant subspaces on Hardy and Bergman spaces of the unit ball or polydisk
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 68 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 232-245
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Uchenna Okeja. Deliberative Agency: A Study in Modern African Political Philosophy. Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press, 2022. $30. Paper. ISBN: 9780253059918.
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 67 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 1074-1076
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The moth fauna is more diverse in the understorey than in the canopy in a European forest
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 115 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation