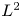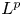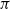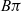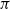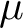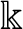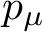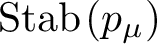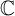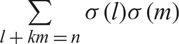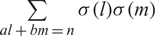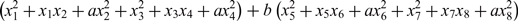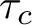Refine search
Actions for selected content:
25847 results in Abstract analysis
Global well-posedness and nonlinear stability of a chemotaxis system modelling multiple sclerosis
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 4 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 July 2021, pp. 826-856
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation

Numerical Ranges of Hilbert Space Operators
-
- Published online:
- 27 July 2021
- Print publication:
- 05 August 2021
Lower bound on the size of a quasirandom forcing set of permutations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 31 / Issue 2 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 July 2021, pp. 304-319
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
COMPARISON OF KUMMER LOGARITHMIC TOPOLOGIES WITH CLASSICAL TOPOLOGIES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 July 2021, pp. 1087-1117
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
THE BOREL CHARACTER
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 22 / Issue 2 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 July 2021, pp. 747-797
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Spectral gap in random bipartite biregular graphs and applications
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 31 / Issue 2 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 July 2021, pp. 229-267
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Asymptotic stability of rarefaction wave for the compressible Navier‐Stokes‐Korteweg equations in the half space
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 July 2021, pp. 756-779
- Print publication:
- June 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
TOPOLOGICAL 4-MANIFOLDS WITH 4-DIMENSIONAL FUNDAMENTAL GROUP
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 64 / Issue 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 July 2021, pp. 454-461
-
- Article
- Export citation
ON NONCRITICAL GALOIS REPRESENTATIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 22 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2021, pp. 383-420
- Print publication:
- January 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
PETERZIL–STEINHORN SUBGROUPS AND
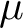 $\mu $-STABILIZERS IN ACF
$\mu $-STABILIZERS IN ACF
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 July 2021, pp. 1003-1022
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
NORMAL REFLECTION SUBGROUPS OF COMPLEX REFLECTION GROUPS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 22 / Issue 2 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 July 2021, pp. 879-917
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Perfect matchings, rank of connection tensors and graph homomorphisms
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 31 / Issue 2 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2021, pp. 268-303
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
EULER CLASSES: SIX-FUNCTORS FORMALISM, DUALITIES, INTEGRALITY AND LINEAR SUBSPACES OF COMPLETE INTERSECTIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 22 / Issue 2 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2021, pp. 681-746
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
EVALUATION OF CONVOLUTION SUMS
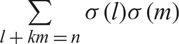 $$\sum\limits_{l + km = n} {\sigma (l)\sigma (m)} $$ AND
$$\sum\limits_{l + km = n} {\sigma (l)\sigma (m)} $$ AND 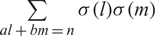 $$\sum\limits_{al + bm = n} {\sigma (l)\sigma (m)} $$ FOR k = a · b = 21, 33, AND 35
$$\sum\limits_{al + bm = n} {\sigma (l)\sigma (m)} $$ FOR k = a · b = 21, 33, AND 35
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 64 / Issue 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2021, pp. 434-453
-
- Article
- Export citation
PRM volume 151 issue 4 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 151 / Issue 4 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 July 2021, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- August 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
PRM volume 151 issue 4 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 151 / Issue 4 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 July 2021, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- August 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Wold decomposition on odometer semigroups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 July 2021, pp. 738-755
- Print publication:
- June 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
THE GENERIC FIBRE OF MODULI SPACES OF BOUNDED LOCAL G-SHTUKAS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 22 / Issue 2 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2021, pp. 799-878
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
GEOMETRICAL AND MEASURE-THEORETIC STRUCTURES OF MAPS WITH A MOSTLY EXPANDING CENTER
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 22 / Issue 2 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2021, pp. 919-959
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
ON THE EXISTENCE OF NON-NORM-ATTAINING OPERATORS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 22 / Issue 3 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 July 2021, pp. 1023-1035
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation