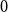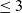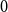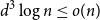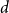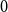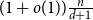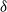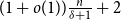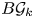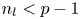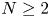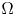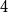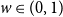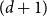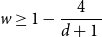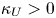Refine search
Actions for selected content:
25820 results in Abstract analysis
Improved bound for improper colourings of graphs with no odd clique minor
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 2 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2022, pp. 326-333
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
PONTRYAGIN DUALITY FOR VARIETIES OVER p-ADIC FIELDS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 23 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 September 2022, pp. 425-462
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Local well-posedness and global analyticity for solutions of a generalized 0-equation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2022, pp. 1630-1650
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Examples of multiparameter CCR flows with non-trivial index
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 65 / Issue 3 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2022, pp. 799-832
-
- Article
- Export citation
Towards the 0-statement of the Kohayakawa-Kreuter conjecture
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 2 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2022, pp. 225-268
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Projective invariants of images
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 34 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2022, pp. 936-946
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
THE STABLE LIMIT DAHA AND THE DOUBLE DYCK PATH ALGEBRA
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 23 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2022, pp. 379-424
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
PRM volume 152 issue 5 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2022, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A characterization of alternating links in thickened surfaces – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2022, p. 1424
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Irregular subgraphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 2 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2022, pp. 269-283
-
- Article
- Export citation
Multiscale linearization of nonautonomous systems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2022, pp. 1609-1629
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
PRM volume 152 issue 5 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2022, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The mod-p homology of the classifying spaces of certain gauge groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2022, pp. 1805-1817
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the optimization of the first weighted eigenvalue
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 September 2022, pp. 1777-1804
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Uniqueness of the Gibbs measure for the 4-state anti-ferromagnetic Potts model on the regular tree
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 32 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2022, pp. 158-182
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nonrigidity of flat ribbons
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2022, pp. 1297-1314
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Coisotropic Ekeland–Hofer capacities
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 September 2022, pp. 1564-1608
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Transportation on spheres via an entropy formula
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 September 2022, pp. 1467-1478
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A note on monotonicity and Bochner formulas in Carnot groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 September 2022, pp. 1543-1563
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
VARIANTS OF A MULTIPLIER THEOREM OF KISLYAKOV
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 23 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, pp. 347-377
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation