Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419635 results in Open Access
Sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia) a legume with great ecological and agronomical potential under climate change
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 162 / Issue 4 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, pp. 307-331
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A DIFFERENTIAL-GEOMETRIC PERSPECTIVE ON MAGNETO-HYDRODYNAMIC EQUILIBRIA
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 111 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, pp. 180-181
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A call for clarity in contractual accessions to shareholder and partnership agreements
-
- Journal:
- Legal Studies / Volume 45 / Issue 1 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, pp. 96-112
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A revisit to the “Rigorous study of propagation in metallic circular waveguide filled with anisotropic metamaterial”
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 16 / Issue 8 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, pp. 1439-1440
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Absolute Fairness and Weighted Lotteries
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Exploitation’s grounding problem
-
- Journal:
- Economics & Philosophy / Volume 41 / Issue 2 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, pp. 357-375
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Morphological and genetic analysis of a rediscovered Clinostomum sp. parasitising Titanolebias monstrosus and Trigonectes aplocheiloides (Cyprinodontiformes: Rivulidae)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 98 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, e74
-
- Article
- Export citation
Uniformity aspects of
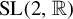 ${\mathrm {SL}}(2,{\mathbb R})$ cocycles and applications to Schrödinger operators defined over Boshernitzan subshifts
${\mathrm {SL}}(2,{\mathbb R})$ cocycles and applications to Schrödinger operators defined over Boshernitzan subshifts
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 45 / Issue 6 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, pp. 1734-1756
- Print publication:
- June 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Tim Summers, The Legend of Zelda: Ocarina of Time: A Game Music Companion, Studies in Game Sound and Music (Intellect Books, 2021)
-
- Journal:
- Royal Musical Association Research Chronicle / Volume 54 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, pp. 141-153
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
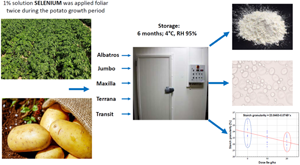
Yield and quality of potato starch depending on genotype, selenium fertilization and storage time
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 162 / Issue 4 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, pp. 332-342
-
- Article
- Export citation
Three-dimensional clustering characteristics of large-Stokes-number dilute sprays interacting with turbulent swirling co-flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 999 / 25 November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, A73
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of time-restricted eating on body composition, biomarkers of metabolism, inflammation, circadian system and oxidative stress in overweight and obesity: an exploratory review
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
From Cultural Property to Cultural Heritage
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Cultural Property / Volume 31 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Considering heterogeneity within negative emotionality can inform the distinction between diathesis-stress and differential susceptibility: Children’s early anger and fear as moderators of effects of parental socialization on antisocial conduct
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 37 / Issue 4 / October 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, pp. 2138-2150
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mean field control of droplet dynamics with high-order finite-element computations
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 999 / 25 November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, A76
-
- Article
- Export citation
Arithmetic Ramsey theory over the primes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, pp. 1-47
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Taxonomic summary of Schyzocotyle (Cestoda: Bothriocephalidae) with a redescription of Schyzocotyle nayarensis (Malhotra, 1983) from India
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 98 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, e73
-
- Article
- Export citation
An Homage to Dan Morin, 16 June 1948–29 July 2024
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 52 / Issue 2 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, p. 171
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Global existence of a weak solution for a reaction–diffusion system in a porous medium with membrane conditions and mass control
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 77 / Issue 6 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, pp. 2006-2028
- Print publication:
- December 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Exercise combined with vitamin D supplementation has additive health effects on short physical performance battery and stair climbing in older adults: a scope review of randomised controlled trials
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 133 / Issue 1 / 14 January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, pp. 48-57
- Print publication:
- 14 January 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation