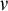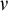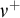Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419596 results in Open Access
Michael Ng, Political Censorship in British Hong Kong: Freedom of Expression and the Law (1842–1997) Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2022. Pp. xiv + 211. Hardcover $39.99 (ISBN 9781108830027). doi:10.1017/9781108908580
-
- Journal:
- Law and History Review / Volume 41 / Issue 4 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, pp. 846-849
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Anne-Maria Makhulu. Making Freedom: Apartheid, Squatter Politics, and the Struggle for Home. Durham: Duke University Press, 2015. xxiii + 256 pp. Illustrations. Index. $26.95 Paper. 978-0-8223-5966-1.
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 66 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, pp. 1089-1091
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The influence of spectral bandwidth and shape on deep-water wave breaking onset
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, A14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Trauma in childhood: therapeutic implications of the differences between early-life and late-life suicidal behavior: Commentary on “Childhood trauma is associated with early-onset but not late-onset suicidal behavior in late-life depression” by Chang and associates
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 36 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, pp. 326-328
-
- Article
- Export citation
Climatic and cave settings influence on drip water fluorescent organic matter with implications for fluorescent laminations in stalagmites
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 118 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, pp. 41-61
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association of the timing of evening eating with BMI Z-score and waist-to-height ratio among preschool-aged children in Finland
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 5 / 14 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, pp. 911-920
- Print publication:
- 14 March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Joint effects between cadmium exposure and dietary antioxidant quality score on osteoporosis and bone mineral density
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, pp. 956-963
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Socioeconomic position, modifiable dementia risk and cognitive decline: results of 12-year Maastricht Aging Study
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 36 / Issue 7 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, pp. 574-586
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A large-deviation principle for birth–death processes with a linear rate of downward jumps
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 61 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, pp. 781-801
- Print publication:
- September 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
George di Giovanni, Hegel and the Challenge of Spinoza: A Study in German Idealism, 1801-1831. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021. ISBN: 978-11088-4224-2 (hbk), 978-11088-2040-0 (pbk), 978-1-108-90699-9 (pdf). Pp. 259. £75.00.
-
- Journal:
- Hegel Bulletin / Volume 46 / Issue 2 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, pp. 422-428
- Print publication:
- August 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Who consumes ultra-processed food? A systematic review of sociodemographic determinants of ultra-processed food consumption from nationally representative samples
-
- Journal:
- Nutrition Research Reviews / Volume 37 / Issue 2 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, pp. 416-456
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Historical Gender Gap Index: A Longitudinal and Spatial Assessment of Sweden, 1870–1990
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Economic History / Volume 83 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 October 2023, pp. 943-980
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Tibor Valuch. Everyday Life under Communism and After: Lifestyle and Consumption in Hungary, 1945–2000 Budapest: Central European University Press, 2021. Pp. 508.
-
- Journal:
- Austrian History Yearbook / Volume 55 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 October 2023, pp. 507-508
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
The art of gathering: histories of international scientific conferences
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal for the History of Science / Volume 56 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 October 2023, pp. 423-433
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Orientations de facilitation pour soutenir l’application de l’Algo dans les services de soutien à domicile des personnes aînées
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement / Volume 43 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 October 2023, pp. 167-175
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
STATIONARY REFLECTION AND THE FAILURE OF THE SCH
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Symbolic Logic / Volume 89 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. 1-26
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Taylorism, Worker Resistance, and Industrial Relations in Sweden
-
- Journal:
- International Review of Social History / Volume 68 / Issue 3 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. 429-451
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Differential Harnack estimates for a weighted nonlinear parabolic equation under a super Perelman–Ricci flow and implications
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. 687-717
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Virtual Reality Visualization of an Epidermoid Cyst Causing Intracranial Hypertension
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. 886-887
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
“Hummingbird Sign” Associated with Obstructive Hydrocephalus Due to Aqueductal Web
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue 5 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. 681-682
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation