Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419572 results in Open Access
HOW TO NAME A TRIREME
-
- Journal:
- Annual of the British School at Athens / Volume 119 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 419-434
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
INS volume 29 issue 8 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue 8 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. f1-f4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Animal proverbs: A cross-cultural perspective
-
- Journal:
- English Today / Volume 40 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 231-236
- Print publication:
- September 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Lake Ladoga. The coastal history of the greatest lake in Europe. Maria Lähteenmäki and Isaac Land, editors. Helsinki: Finnish Literary Society, SKS. 2023. 233 p, paperback, epub and pdf. ISBN 978-951-858-628-2 (print). €45. Also available as a free open-access download (https://doi.org/10.21435/sfh.27).
-
- Journal:
- Polar Record / Volume 59 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, e30
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Intersection configurations in free and free times free-abelian groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 154 / Issue 5 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 1552-1582
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
JAZ volume 115 issue 2 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 115 / Issue 2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Responsibility Skeptics Should Be More Skeptical
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Philosophy / Volume 53 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 95-100
-
- Article
- Export citation
The trace-element compositions of amphibole, magnetite and ilmenite as potential exploration guides to metamorphosed Proterozoic Cu–Zn±Pb±Au±Ag volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits in Colorado, USA
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 88 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 61-89
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Asymptotic formulas of the eigenvalues for the linearization of the scalar field equation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 307-344
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Late glacial through Early Holocene environments inferred using pollen from coprolites and sediments recovered from Paisley Caves, Oregon
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 116 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 78-95
-
- Article
- Export citation
VALID HETEROSKEDASTICITY ROBUST TESTING
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 41 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 249-301
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Replacing red and processed meat with lean or fatty fish and all-cause and cause-specific mortality in Norwegian women. The Norwegian Women and Cancer Study (NOWAC): a prospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 3 / 14 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 531-543
- Print publication:
- 14 February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Problems for generalized Monge–Ampère equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 67 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 265-278
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Public services and the urban middling sort: the provision of water in Bristol, Chester and Ipswich, 1540–1640
-
- Journal:
- Urban History / Volume 51 / Issue 3 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 500-518
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ON COHEN AND PRIKRY FORCING NOTIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Symbolic Logic / Volume 89 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 858-904
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A “Patient Preference” Model of Recruitment for Research from Primary-Care-Based Memory Clinics: A Promising New Approach
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement / Volume 43 / Issue 2 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 275-286
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
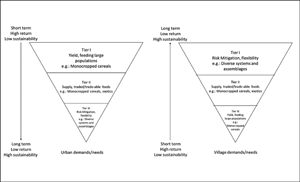
Different strategies in Indus agriculture: the goals and outcomes of farming choices
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Constrained read-once refutations in UTVPI constraint systems: A parallel perspective
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Structures in Computer Science / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 227-243
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Navigating the Storm: An Exquisite Leadership Insight into Healthcare Management amidst the COVID-19 Pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, e484
-
- Article
- Export citation
Language proficiency modulates L2 orthographic learning mechanism: Evidence from event-related brain potentials in overt naming
-
- Journal:
- Studies in Second Language Acquisition / Volume 46 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 119-140
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation