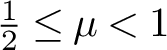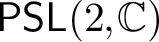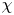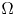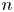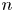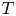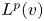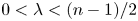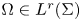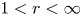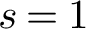Refine search
Actions for selected content:
25839 results in Abstract analysis
SPECTRAL INEQUALITIES FOR COMBINATIONS OF HERMITE FUNCTIONS AND NULL-CONTROLLABILITY FOR EVOLUTION EQUATIONS ENJOYING GELFAND–SHILOV SMOOTHING EFFECTS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 22 / Issue 6 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2022, pp. 2533-2582
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Laplace transform approach to direct and inverse problems for multi-compartment models
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 33 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 March 2022, pp. 1170-1184
-
- Article
- Export citation
Data-driven entropic spatially inhomogeneous evolutionary games
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 34 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2022, pp. 106-159
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
PEM series 2 volume 65 issue 1 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 65 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2022, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
PEM series 2 volume 65 issue 1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 65 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2022, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
QUASI-ISOMETRIC EMBEDDINGS INAPPROXIMABLE BY ANOSOV REPRESENTATIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 22 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2022, pp. 2497-2514
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Variational model with nonstandard growth conditions for restoration of satellite optical images using synthetic aperture radar
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 34 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 March 2022, pp. 77-105
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation

Matrix Analysis and Entrywise Positivity Preservers
-
- Published online:
- 10 March 2022
- Print publication:
- 31 March 2022
Relaxation for an optimal design problem in BD(Ω)
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 March 2022, pp. 721-763
- Print publication:
- June 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Generalized Bloch type periodicity and applications to semi-linear differential equations in banach spaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 65 / Issue 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2022, pp. 326-355
-
- Article
- Export citation
Locations of interior transition layers to inhomogeneous transition problems in higher -dimensional domains
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2022, pp. 764-783
- Print publication:
- June 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
A note on holomorphic sectional curvature of a hermitian manifold
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 64 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 March 2022, pp. 739-745
-
- Article
- Export citation
Refined universality for critical KCM: lower bounds
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 31 / Issue 5 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 March 2022, pp. 879-906
-
- Article
- Export citation
Measure data elliptic problems with generalized Orlicz growth
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 March 2022, pp. 588-618
- Print publication:
- April 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Jump phenomena of the n-th eigenvalue of discrete Sturm–Liouville problems with application to the continuous case
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 March 2022, pp. 619-653
- Print publication:
- April 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Pirashvili-type theorem for functors on non-empty finite sets
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 65 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 March 2022, pp. 1-61
-
- Article
- Export citation
Weighted estimates for Bochner–Riesz operators on Lorentz spaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2022, pp. 654-678
- Print publication:
- April 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
VALUES OF ZETA FUNCTIONS OF ARITHMETIC SURFACES AT
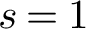 $s=1$
$s=1$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 22 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2022, pp. 2455-2496
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
JMJ volume 21 issue 2 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 21 / Issue 2 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2022, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- March 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Approximation numbers of composition operators on weighted besov spaces of analytic functions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 65 / Issue 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2022, pp. 311-325
-
- Article
- Export citation