Refine search
Actions for selected content:
25814 results in Abstract analysis
Existence and analyticity of solutions of the Kuramoto–Sivashinsky equation with singular data
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, pp. 1-26
-
- Article
- Export citation
Arithmetic Ramsey theory over the primes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, pp. 1-47
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Differential embeddings into algebras of topological stable rank 1
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, pp. 1-25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fractional order for the transmission dynamics of coffee berry diseases (CBD)
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 36 / Issue 4 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, pp. 879-896
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Long induced paths in expanders
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, pp. 276-282
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Noisy group testing via spatial coupling
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 November 2024, pp. 210-258
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Maximal noncompactness of limiting Sobolev embeddings
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 November 2024, pp. 1-19
-
- Article
- Export citation
CYT and SKT manifolds with parallel Bismut torsion
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 November 2024, pp. 1-26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Product of polynomial values being large power
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 68 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 November 2024, pp. 51-62
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The socle of subshift algebras, with applications to subshift conjugacy
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 November 2024, pp. 1-26
-
- Article
- Export citation
Additive energies of subsets of discrete cubes
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 November 2024, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Principal bundle structure of the space of metric measure spaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 November 2024, pp. 1-31
-
- Article
- Export citation
General study on limit cycle bifurcation near a double eight figure loop
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 November 2024, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
- Export citation
Liouville theorems for the sub-linear Lane–Emden equation on the half space
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 November 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
- Export citation
Travelling wave solutions and spreading speeds for a scalar age-structured equation with nonlocal diffusion
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 36 / Issue 4 / August 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2024, pp. 856-878
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Centers of Artin groups defined on cones
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 68 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2024, pp. 44-50
-
- Article
- Export citation
Series expansion, higher-order monotonicity properties and inequalities for the modulus of the Grötzsch ring
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 68 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2024, pp. 16-43
-
- Article
- Export citation
QUASI-ERGODICITY OF COMPACT STRONG FELLER SEMIGROUPS ON
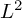 $L^2$
$L^2$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 24 / Issue 2 / March 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 November 2024, pp. 541-584
- Print publication:
- March 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Simplicity of non-associative skew Laurent polynomial rings
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 68 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2024, pp. 1-15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Maximal operators along flat curves with one variable vector field
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 67 / Issue 4 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2024, pp. 1212-1228
-
- Article
- Export citation















































 . We discuss several applications and illustrate our results with examples. This includes a complete description of quasi-ergodicity for a large class of semigroups corresponding to non-local Schrödinger operators with confining potentials.
. We discuss several applications and illustrate our results with examples. This includes a complete description of quasi-ergodicity for a large class of semigroups corresponding to non-local Schrödinger operators with confining potentials.




