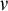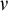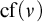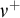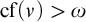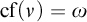Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419506 results in Open Access
Who consumes ultra-processed food? A systematic review of sociodemographic determinants of ultra-processed food consumption from nationally representative samples
-
- Journal:
- Nutrition Research Reviews / Volume 37 / Issue 2 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, pp. 416-456
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Historical Gender Gap Index: A Longitudinal and Spatial Assessment of Sweden, 1870–1990
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Economic History / Volume 83 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 October 2023, pp. 943-980
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Tibor Valuch. Everyday Life under Communism and After: Lifestyle and Consumption in Hungary, 1945–2000 Budapest: Central European University Press, 2021. Pp. 508.
-
- Journal:
- Austrian History Yearbook / Volume 55 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 October 2023, pp. 507-508
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
The art of gathering: histories of international scientific conferences
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal for the History of Science / Volume 56 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 October 2023, pp. 423-433
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Orientations de facilitation pour soutenir l’application de l’Algo dans les services de soutien à domicile des personnes aînées
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement / Volume 43 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 October 2023, pp. 167-175
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
STATIONARY REFLECTION AND THE FAILURE OF THE SCH
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Symbolic Logic / Volume 89 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. 1-26
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Taylorism, Worker Resistance, and Industrial Relations in Sweden
-
- Journal:
- International Review of Social History / Volume 68 / Issue 3 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. 429-451
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Differential Harnack estimates for a weighted nonlinear parabolic equation under a super Perelman–Ricci flow and implications
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. 687-717
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Virtual Reality Visualization of an Epidermoid Cyst Causing Intracranial Hypertension
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. 886-887
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
“Hummingbird Sign” Associated with Obstructive Hydrocephalus Due to Aqueductal Web
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue 5 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. 681-682
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Webs of type P
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 76 / Issue 6 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. 1917-1966
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Le sel en Maurétanie césarienne et en Numidie. Quels gisements ? Quels usages ? Quels réseaux ?
-
- Journal:
- Libyan Studies / Volume 54 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. 8-21
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Inca Mitmaqkuna, Chaînes Opératoires, and Pottery Production in the Northern Andes
-
- Journal:
- Latin American Antiquity / Volume 35 / Issue 4 / December 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. 889-906
- Print publication:
- December 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
The authors’ reply to Schaffzin et al’s Letter to the Editor
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 12 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, p. 2098
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Innovation Under Ambiguity and Risk
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis / Volume 59 / Issue 7 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. 3190-3229
- Print publication:
- November 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dynamics and proliferation of turbulent stripes in plane-Poiseuille and plane-Couette flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, A21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Isabel Hofmeyr. Dockside Reading: Hydrocolonialism and the Custom House. Durham: Duke University Press, 2022. xii + 121 pp. Illustrations. Bibliography. Index. $22.95 Paper. ISBN: 978-1478017745.
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 66 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. 1078-1080
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Marco Tamborini, The Architecture of Evolution: The Science of Form in Twentieth-Century Evolutionary Biology Pittsburgh: University of Pittsburgh Press, 2022. Pp. 283. ISBN: 978-0-8229-4735-6. $455.00 (hardcover).
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal for the History of Science / Volume 56 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. 591-593
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
PARTITIONS OF NATURAL NUMBERS AND THEIR WEIGHTED REPRESENTATION FUNCTIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 110 / Issue 1 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. 12-18
- Print publication:
- August 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nutrition and immunity: lessons from coronavirus disease-2019
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 84 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. 8-23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation