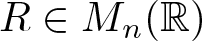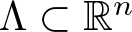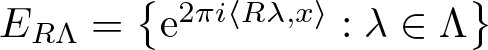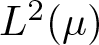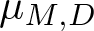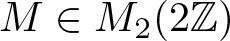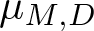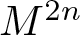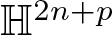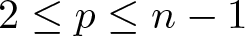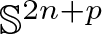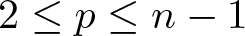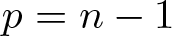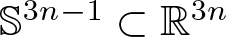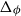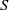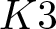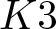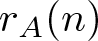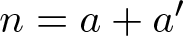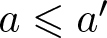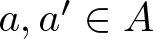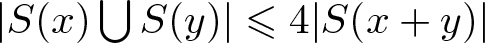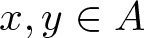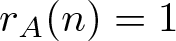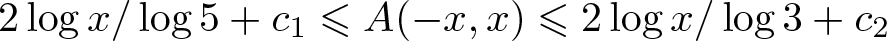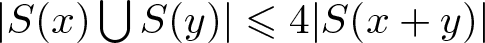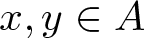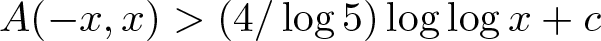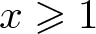Refine search
Actions for selected content:
25816 results in Abstract analysis
Remarks on countable subadditivity
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 154 / Issue 5 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 August 2023, pp. 1504-1517
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Proper Ehresmann semigroups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 August 2023, pp. 758-788
-
- Article
- Export citation
New mock theta functions and formulas for basic hypergeometric series
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 August 2023, pp. 868-896
-
- Article
- Export citation
The spectral eigenmatrix problems of planar self-affine measures with four digits
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 August 2023, pp. 897-918
-
- Article
- Export citation
Corrigendum: Von Neumann algebras and extensions of inverse semigroups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 August 2023, pp. 919-922
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Kaehler submanifolds of the real hyperbolic space
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 August 2023, pp. 810-831
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The topology of compact rank-one ECS manifolds
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 August 2023, pp. 789-809
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Toeplitz determinants with a one-cut regular potential and Fisher–Hartwig singularities I. Equilibrium measure supported on the unit circle
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 154 / Issue 5 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 August 2023, pp. 1431-1472
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the Jones polynomial modulo primes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 65 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 August 2023, pp. 730-734
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Spreading dynamics of a diffusive epidemic model with free boundaries and two delays
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 34 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 August 2023, pp. 1133-1169
-
- Article
- Export citation
On classification of singular matrix difference equations of mixed order
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 154 / Issue 4 / August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 August 2023, pp. 1235-1258
- Print publication:
- August 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Quasipolynomial-time algorithms for Gibbs point processes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 August 2023, pp. 1-15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the structure of lower bounded HNN extensions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 65 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2023, pp. 697-715
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
JMJ volume 22 issue 5 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 22 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2023, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
JMJ volume 22 issue 5 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 22 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2023, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Exact formulae and Turán inequalities for Vafa–Witten invariants of
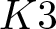 $K3$ surfaces
$K3$ surfaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 August 2023, pp. 845-861
-
- Article
- Export citation
Characterising small objects in the regime between the eddy current model and wave propagation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 35 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 August 2023, pp. 294-317
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The effect of pore-scale contaminant distribution on the reactive decontamination of porous media
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 35 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 August 2023, pp. 318-358
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Every Salem number is a difference of two Pisot numbers
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 August 2023, pp. 862-867
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the density of bounded bases
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 August 2023, pp. 832-844
-
- Article
- Export citation