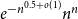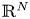Refine search
Actions for selected content:
25816 results in Abstract analysis
Periodic solutions of four-order degenerate differential equations with finite delay in vector-valued function spaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2023, pp. 395-412
- Print publication:
- April 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Editorial “Symmetries and differential equations”
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 34 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, pp. 911-912
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The non-autonomous Navier–Stokes–Brinkman–Forchheimer equation with Dirichlet boundary conditions: dissipativity, regularity, and attractors
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, pp. 352-393
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Stabilization of the Kawahara–Kadomtsev–Petviashvili equation with time-delayed feedback
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 280-306
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Intersection configurations in free and free times free-abelian groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 154 / Issue 5 / October 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 1552-1582
- Print publication:
- October 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Asymptotic formulas of the eigenvalues for the linearization of the scalar field equation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 307-344
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Order continuity of Arens extensions of regular multilinear operators
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 258-279
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Fixed point conditions for non-coprime actions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 345-351
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
PRM volume 153 issue 5 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On the size of maximal intersecting families
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, pp. 32-49
-
- Article
- Export citation
PRM volume 153 issue 5 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 153 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2023, pp. f1-f2
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
PEM series 2 volume 66 issue 3 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2023, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
PEM series 2 volume 66 issue 3 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2023, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Stability properties of multidimensional symmetric hyperbolic systems with damping, differential constraints and delay
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2023, pp. 199-241
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the dimension of planar self-affine sets with non-invertible maps
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2023, pp. 242-257
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the linearized Whitham–Broer–Kaup system on bounded domains
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2023, pp. 104-123
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Periodic and solitary waves in a Korteweg–de Vries equation with delay
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2023, pp. 176-198
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
A weighted Trudinger–Moser inequalities and applications to some weighted $(N,q)-$
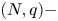 Laplacian equation in $\mathbb {R}^N$
Laplacian equation in $\mathbb {R}^N$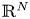 with new exponential growth conditions
with new exponential growth conditions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2023, pp. 124-175
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Coupling capacity in C*-algebras
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 1 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2023, pp. 81-103
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Reidemeister spectrum of finite abelian groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 4 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2023, pp. 940-959
-
- Article
- Export citation