Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1381678 results in Open Access
EURIPIDES, PROTESILAVS FR. 646A KANNICHT
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Quarterly , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2026, pp. 1-4
-
- Article
- Export citation
Transient biventricular collapse after atrial septal defect closure in an adolescent: a diastolic dysfunction-driven paradox
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2026, pp. 1-4
-
- Article
- Export citation
Geopolitics of Rare Earth Elements (REE) in the Arctic: Study of evolving strategic, scholar, and media discourse
-
- Journal:
- Polar Record / Volume 62 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2026, e3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Infinite dimensional metapopulation SIS model with generalized incidence rate
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2026, pp. 1-45
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Experimental luthiery in Latin America: A postcolonial and acoustemological approach
-
- Journal:
- Organised Sound , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2026, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
“Unconscious Stipendiaries of This Wicked System”? Female Enslavers and Compensation in Nineteenth-century Britain
-
- Journal:
- Journal of British Studies / Volume 65 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2026, e3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The cold tolerance of an adult winter-active stonefly: how Allocapnia pygmaea (Plecoptera: Capniidae) avoids freezing in winter in Nova Scotia, Canada
-
- Journal:
- The Canadian Entomologist / Volume 158 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2026, e3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
SIMULTANEOUS BOUNDING OF
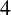 $4$-RANKS IN NARROW CLASS GROUPS OF QUADRATIC FIELDS
$4$-RANKS IN NARROW CLASS GROUPS OF QUADRATIC FIELDS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2026, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
- Export citation
Noncompaction and dilated cardiomyopathy in carvajal syndrome – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2026, p. 1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Eastward, Westward: A Life in Law Jerome A. Cohen. New York: Columbia University Press, 2025. 384 pp. $38.00; £32.00 (hbk). ISBN 9780231215923
-
- Journal:
- The China Quarterly , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2026, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
Semi-Synthetic Cannabinoids Remain a Potent Concern in Ireland
-
- Journal:
- Irish Journal of Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2026, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Expanding the machine: Notating generative synthesis with a state-based representation and a navigable timbre space
-
- Journal:
- Organised Sound , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2026, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
List of Reviewers
-
- Journal:
- American Political Science Review / Volume 120 / Issue 1 / February 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2026, pp. 392-398
- Print publication:
- February 2026
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Ingroup Favoritism? Explaining Intergroup Bias in Trait Evaluations among Members of an Ethnolinguistic Minority in Finland
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Race, Ethnicity and Politics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2026, pp. 1-24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
MODULAR ELEMENTS IN THE LATTICE OF MONOID VARIETIES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2026, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Corpus linguistics and AI in the reconfiguration of language learning ecologies
-
- Journal:
- Language Teaching , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2026, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
FRAGMENTS AND INCOMPLETE TEXTS - Jacqueline Fabre-serris / Marco Formisano / Stavros Frangoulidis (edd.), Labor Imperfectus. Unfinished, Incomplete, Partial Texts in Classical Antiquity. (Trends in Classics Supplementary Volume 157.) Pp. xii + 432, ills. Berlin and Boston: De Gruyter, 2024. Cased, £123.50. ISBN: 978-3-11-134079-1. - Nora Goldschmidt, Fragmentary Modernism. The Classical Fragment in Literary and Visual Cultures, c.1896–c.1936. Pp. xvi + 222, b/w & colour ills. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2023. Cased, £80. ISBN: 978-0-19-286340-9.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2026, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
INDEPENDENCE AND INDUCTION IN REVERSE MATHEMATICS
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Symbolic Logic / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2026, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Time frames: Crisis expertise and rapid response mechanisms
-
- Journal:
- Review of International Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2026, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Connecting Places to the Inca World: Exploring the Significance of Capacocha-Related Offerings at Lake Titicaca and Pachacamac
-
- Journal:
- Latin American Antiquity , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2026, pp. 1-19
-
- Article
- Export citation