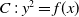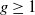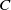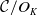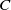Refine search
Actions for selected content:
25814 results in Abstract analysis
Measuring multidimensional heterogeneity in emergent social phenomena
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 36 / Issue 2 / April 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2024, pp. 316-327
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Minimal monoids generating varieties with complex subvariety lattices
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 67 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2024, pp. 617-642
-
- Article
- Export citation
Triangular matrix categories over quasi-hereditary categories
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / September 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2024, pp. 449-470
- Print publication:
- September 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Limit cycles in a rotated family of generalized Liénard systems allowing for finitely many switching lines
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 6 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2024, pp. 2121-2149
- Print publication:
- December 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the structure of some one-generator braces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 67 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 March 2024, pp. 566-576
-
- Article
- Export citation
Global index of real polynomials
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 6 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2024, pp. 2020-2048
- Print publication:
- December 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
A mathematical analysis of the Kakinuma model for interfacial gravity waves. Part II: justification as a shallow water approximation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 6 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2024, pp. 2049-2120
- Print publication:
- December 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Models and integral differentials of hyperelliptic curves
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 66 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2024, pp. 382-439
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
L2 to Lp bounds for spectral projectors on the Euclidean two-dimensional torus
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 67 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 March 2024, pp. 431-459
-
- Article
- Export citation
THERMODYNAMIC FORMALISM FOR AMENABLE GROUPS AND COUNTABLE STATE SPACES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 23 / Issue 6 / November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 March 2024, pp. 2647-2711
- Print publication:
- November 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Eternal solutions to a porous medium equation with strong non-homogeneous absorption. Part I: radially non-increasing profiles
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 6 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2024, pp. 1998-2019
- Print publication:
- December 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Canonical decompositions and algorithmic recognition of spatial graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 67 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2024, pp. 388-430
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the moduli of hypersurfaces in toric orbifolds
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 67 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2024, pp. 577-616
-
- Article
- Export citation
Decay at infinity for solutions to some fractional parabolic equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 6 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2024, pp. 1961-1997
- Print publication:
- December 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
Examples of hyperbolic spaces without the properties of quasi-ball or bounded eccentricity
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 66 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 March 2024, pp. 440-448
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Necessary and sufficient conditions for ground state solutions to planar Kirchhoff-type equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 5 / October 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 March 2024, pp. 1938-1959
- Print publication:
- October 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
A boundary maximum principle for stationary pairs of varifolds with fixed contact angle
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 67 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2024, pp. 316-335
-
- Article
- Export citation
Unbounded Sturm attractors for quasilinear parabolic equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 67 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2024, pp. 542-565
-
- Article
- Export citation
Structure of generalized Yamabe solitons and its applications
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 67 / Issue 2 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 March 2024, pp. 336-348
-
- Article
- Export citation
Optimal inverse problems of potentials for two given eigenvalues of Sturm–Liouville problems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 155 / Issue 5 / October 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 March 2024, pp. 1914-1937
- Print publication:
- October 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation