Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1761 results in 05xxx
GALOIS GROUPS OF APÉRY-LIKE SERIES MODULO PRIMES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2026, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
SOME MONOCHROMATIC PATTERNS IN NATURAL NUMBERS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2026, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fluid limit of a distributed ledger model with random delay
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2026, pp. 1-41
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Four universal growth regimes in degree-dependent first passage percolation on spatial random graphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 14 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 February 2026, e22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the number of
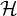 $\mathcal {H}$-free hypergraphs
$\mathcal {H}$-free hypergraphs
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 14 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 February 2026, e20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Generalized percolation games on the two-dimensional square lattice and ergodicity of associated probabilistic cellular automata
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 February 2026, pp. 1-97
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Graphical sequences and plane trees
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 February 2026, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Lorentzian polynomials on cones
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 14 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2026, e16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Random Fibonacci Words via Clone Schur Functions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 14 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2026, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Degeneracy locus formulas for amenable Weyl group elements
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Nagoya Mathematical Journal / Volume 261 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2026, e13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Clique density vs blowups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2026, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Asymmetric infinite sumsets in large sets of integers
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 14 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2026, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Degree-penalized contact processes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 14 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2026, e6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Partitioning theorems for sets of semi-Pfaffian sets, with applications
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 14 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 January 2026, e5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
COMBINATORIAL PROOFS OF CERTAIN RESULTS OF CHEN AND ZOU ON TWO-COLOUR PARTITIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 January 2026, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
- Export citation
Koszul binomial edge ideals
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 14 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, e3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Signature characters of invariant Hermitian forms on irreducible Verma modules of singular infinitesimal character and Hall–Littlewood polynomials
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 January 2026, pp. 1-23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Enriched cycle structures and roots of permutations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Strong discrete Morse theory
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2026, pp. 1-26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Overpartitions with parts separated by parity
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2026, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation