Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1382840 results in Open Access
Yoko Iyeiri, Benjamin Franklin’s English: Form to function analyses (Routledge Studies in Linguistics). London and New York: Routledge, 2025. Pp. 256. ISBN 9781032277042.
-
- Journal:
- English Language & Linguistics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Orienting Work of “Culture” and Africa-China as Method
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, pp. 1-24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A review on the holistic exploration of health benefits and technological advancements in yoghurt incorporating fruit peels
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Dairy Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Innovation under Dynamic Institutional Change: How Firms Can Capture Innovation Opportunities under Institutional Uncertainty
-
- Journal:
- Management and Organization Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, pp. 1-23
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ahmed Nara’s Fatal Mission
-
- Journal:
- African Studies Review / Volume 68 / Issue 4 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, pp. 851-856
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
FROM POLITICS TO THEORY: THE EARLY PUBLIC RECEPTION OF MARX IN BRITAIN, 1885–1887
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the History of Economic Thought , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, pp. 1-29
-
- Article
- Export citation
Bruce Caldwell, John Davis, Uskali Mäki, and Esther-Mirjam Sent, eds., Methodology and History of Economics: Reflections with and without Rules (Oxon/New York: Routledge, 2023), pp. 260, $190 (hardcover). ISBN: 9781032209463.
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the History of Economic Thought , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
First report of the air sac trematode Circumvitellatrema momota (Digenea: Cyclocoelidae) in cracid birds from Central America: pathological findings and phylogenetic confirmation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 100 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, e11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Artificial intelligence and deskilling in medicine
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Critical Analysis of the ICJ’s Ruling in Sudan v. UAE: Genocide Convention Reservations and the Limits of Article IX
-
- Journal:
- Asian Journal of International Law , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Enriched cycle structures and roots of permutations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Sources of variation in microscopic epibiont communities on intertidal rocky organisms in Niigata, Japan
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 106 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, e7
-
- Article
- Export citation
Visualizing Victorian Manchester: Granular Geocoding for Demographic Analysis
-
- Journal:
- Social Science History , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, pp. 1-28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Carl-Ludwig Holtfrerich, Edward A. Tenenbaum and the Deutschmark: How an American Jew Became the Father of Germany’s Postwar Economic Revival (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2024), pp. 794, C$154.95 (hardcover). ISBN: 9781009492812.
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the History of Economic Thought , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
Projecting the Effects of Climate-Driven Migration and Development on Heritage Resources: An Example from the Midwestern United States
-
- Journal:
- American Antiquity , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
- Export citation
Curating the Colonial Past: The “Migrated Archives” and the Struggle for Kenya’s History by Riley Linebaugh, Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 2025. 320 pp.
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Modern African Studies / Volume 63 / Issue 4 / December 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, pp. 296-298
-
- Article
- Export citation
Why has Minsky’s economic theory been ignored?
-
- Journal:
- The Economic and Labour Relations Review ,
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
THE “OFFICIAL OPPONENT”? WASSILY LEONTIEF’S IDEA OF ECONOMETRIC METHODS
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the History of Economic Thought , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, pp. 1-25
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Aftermath of Sovereign Debt Crises: A Narrative Approach
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Economic History , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, pp. 1-40
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The weak-type (1,1) estimate of the
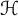 $\mathcal {H}$-harmonic Bergman projection
$\mathcal {H}$-harmonic Bergman projection
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2026, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation