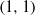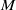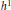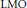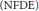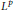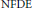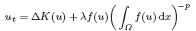Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
308 results in 35Kxx
VORTEX LIQUIDS AND THE GINZBURG–LANDAU EQUATION
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Forum of Mathematics, Sigma / Volume 2 / 01 July 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 May 2014, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A TRANSFORMATION METHOD FOR SOLVING THE HAMILTON–JACOBI–BELLMAN EQUATION FOR A CONSTRAINED DYNAMIC STOCHASTIC OPTIMAL ALLOCATION PROBLEM
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 55 / Issue 1 / July 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 October 2013, pp. 14-38
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Poincaré–Lelong equation via the Hodge–Laplace heat equation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 149 / Issue 11 / November 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 September 2013, pp. 1856-1870
- Print publication:
- November 2013
-
- Article
- Export citation
AN IMPROVED SECOND-ORDER NUMERICAL METHOD FOR THE GENERALIZED BURGERS–FISHER EQUATION
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 54 / Issue 3 / January 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 June 2013, pp. 181-199
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Averaging for a Fully Coupled Piecewise-Deterministic Markov Process in Infinite Dimensions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 44 / Issue 3 / September 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2016, pp. 749-773
- Print publication:
- September 2012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
CRITICAL CURVES FOR A COUPLED SYSTEM OF FAST DIFFUSIVE NEWTONIAN FILTRATION EQUATIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 86 / Issue 3 / December 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 June 2012, pp. 440-447
- Print publication:
- December 2012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A COMPARISON OF CRITICAL TIME DEFINITIONS IN MULTILAYER DIFFUSION
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 52 / Issue 4 / April 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 March 2012, pp. 333-358
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
DOMAIN PERTURBATION FOR PARABOLIC EQUATIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 85 / Issue 1 / February 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 December 2011, pp. 174-176
- Print publication:
- February 2012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
INHOMOGENEOUS PERIODIC PARABOLIC PROBLEMS WITH INDEFINITE DATA
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 84 / Issue 3 / December 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2011, pp. 516-524
- Print publication:
- December 2011
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Very slow grow-up of solutions of a semi-linear parabolic equation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / June 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2011, pp. 381-400
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
TRAVELLING WAVE SOLUTIONS FOR DOUBLY DEGENERATE REACTION–DIFFUSION EQUATIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 52 / Issue 1 / July 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 March 2011, pp. 101-109
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ON THE STABILITY OF STATIONARY LINE AND GRIM REAPER IN PLANAR CURVATURE FLOW
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 83 / Issue 2 / April 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2011, pp. 177-188
- Print publication:
- April 2011
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
FOURTH ORDER GEOMETRIC EVOLUTION EQUATIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 82 / Issue 3 / December 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 November 2010, pp. 523-524
- Print publication:
- December 2010
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A NOTE ON THE NUMERICAL APPROACH FOR THE REACTION–DIFFUSION PROBLEM WITH A FREE BOUNDARY CONDITION
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 51 / Issue 3 / January 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2010, pp. 317-330
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ON THE ISOPERIMETRIC PROBLEM FOR THE LAPLACIAN WITH ROBIN AND WENTZELL BOUNDARY CONDITIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 82 / Issue 2 / October 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 August 2010, pp. 348-350
- Print publication:
- October 2010
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
TRAVELLING WAVE SOLUTIONS IN NONLOCAL REACTION–DIFFUSION SYSTEMS WITH DELAYS AND APPLICATIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 51 / Issue 1 / July 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 March 2010, pp. 49-66
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Energy Functionals and Complex Monge–Ampère Equations
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu / Volume 9 / Issue 3 / July 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 February 2010, pp. 463-476
- Print publication:
- July 2010
-
- Article
- Export citation
Interior h1 Estimates for Parabolic Equations with LMO Coefficients
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 62 / Issue 1 / 01 February 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2018, pp. 202-217
- Print publication:
- 01 February 2010
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Projectors on the Generalized Eigenspaces for Neutral Functional Differential Equations in Lp Spaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics / Volume 62 / Issue 1 / 01 February 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2018, pp. 74-93
- Print publication:
- 01 February 2010
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Existence and blow-up of solutions for a non-local filtration and porous medium problem
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 53 / Issue 1 / February 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 January 2010, pp. 195-209
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation