Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
2107942 results in Journals
Equilibrium states of rotating turbulence in a closed basin with topography
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1029 / 25 February 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, A27
-
- Article
- Export citation
CIVIL WAR AND AUTOCRACY IN ROME - Dominik Maschek, The Roman Civil Wars. The Archaeology and History of a Crisis. Translated by Joseph O’Donnell. Pp. x + 416, figs, ills, maps. Liverpool: Liverpool University Press, 2025 (originally published as Die römischen Bürgerkriege, 2018). Cased, £120. ISBN: 978-1-83624-338-0. - David Potter, Master of Rome. A Life of Julius Caesar. Pp. xx + 374, maps, colour pls. New York: Oxford University Press, 2025. Cased, £22.99. ISBN: 978-0-19-086718-8.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-5
-
- Article
- Export citation
Monetary policy, heterogeneous expectations, and the return of high inflation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Macroeconomic Dynamics / Volume 30 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, e15
-
- Article
- Export citation
Union Citizenship as a Status of Political Integration: ECJ Case C-808/21, Commission v Czech Republic and Case C-814/21, Commission v Poland
-
- Journal:
- European Constitutional Law Review , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2026, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Thecate stem medusozoan polyp from the Upper Ordovician of Québec
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2026, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Vitamin A intake and status, and associations with iron status, anaemia, and birth outcomes of pregnant women in the Free State Province, South Africa: The NuEMI study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2026, pp. 1-32
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Beyond bilingual and monolingual: Cognitive, language and demographic profiles of adolescents in the United States
-
- Journal:
- Bilingualism: Language and Cognition , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2026, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
GALOIS GROUPS OF APÉRY-LIKE SERIES MODULO PRIMES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2026, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
‘Inside the belly of the monster’: The politics of race in Britain, transnational anti-colonialism, and the Black Liberation Front
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Global History , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2026, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Victoria Austen. 2023. Analysing the boundaries of the ancient Roman garden: (re)framing the hortus. London: Bloomsbury; 978-1-350-26518-9 hardback £85.
-
- Journal:
- Antiquity , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2026, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
ON PROPERLY
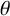 $\theta $-CONGRUENT NUMBERS OVER REAL NUMBER FIELDS
$\theta $-CONGRUENT NUMBERS OVER REAL NUMBER FIELDS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2026, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Using a Participation Monitoring Database to Enhance Recruitment in a Rare Cancer Population
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2026, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Neurorestorative Properties of Ibogaine: Linking Multi-Receptor Affinities to Remyelination and Metabolic Restoration
-
- Journal:
- Acta Neuropsychiatrica / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2026, pp. 1-36
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
SOME MONOCHROMATIC PATTERNS IN NATURAL NUMBERS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2026, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Using targeted spray applications to mitigate herbicide use in corn
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2026, pp. 1-24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Comparison of BLUPF90IOD3 and MiXBLUP implementations of the single-step model applied to the Polish national dairy cattle evaluation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Dairy Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2026, pp. 1-5
-
- Article
- Export citation
A sharp-billed stem ibis from the Fossil Butte Member of the Green River Formation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2026, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Interventions for unpaid carers of people living with breathlessness due to chronic respiratory diseases: Scoping review
-
- Journal:
- Palliative & Supportive Care / Volume 24 / 2026
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2026, e58
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Neonatal Kommerell diverticulum with mid-ductal aneurysmal patent ductus arteriosus: serial imaging documentation of early natural history
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2026, pp. 1-4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Behavioural Insights in Action: Improving Tax Compliance Through Behaviourally Informed Training
-
- Journal:
- Behavioural Public Policy , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2026, pp. 1-15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation